Difference between revisions of "Acne rosacea"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(create) |
(→References: +see also) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Micro=== | ===Micro=== | ||
The sections shows hair-bearing skin with sebaceous hyperplasia and vertically oriented dermal fibrosis. Ther dermis has a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Several epidermal hair follicle cysts are present. Focal giant cell formation is seen. | The sections shows hair-bearing skin with sebaceous hyperplasia and vertically oriented dermal fibrosis. Ther dermis has a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Several epidermal hair follicle cysts are present. Focal giant cell formation is seen. | ||
==See also== | |||
*[[Acne vulgaris]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 18:00, 5 June 2013
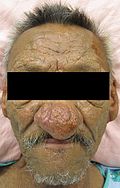
Acne rosacea, also known as rosacea, a common inflammatory skin disorder that uncommonly gets biopsied.[1]
General
- May lead to rhinophyma - large bulbous nose.
Gross
Features:
- Early: erythema, comedones, papules, pustules.
- Late: large bulbous nose with erythema.
Microscopic
Features:
- Perifollicular and perivascular lymphocytes.
- Vascular dilation.
- Folliculitis.
- Dermal fibrosis (late stage).
- Sebaceous gland hyperplasia (late stage).
Sign out
NOSE, DE-BULKING: - COMPATIBLE WITH RHINOPHYMA-ROSACEA SPECTRUM.
Micro
The sections shows hair-bearing skin with sebaceous hyperplasia and vertically oriented dermal fibrosis. Ther dermis has a lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Several epidermal hair follicle cysts are present. Focal giant cell formation is seen.
See also
References
- ↑ Busam, Klaus J. (2009). Dermatopathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 79. ISBN 978-0443066542.