Difference between revisions of "Ganglioneuroma"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(+cat.) |
(split out) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
# | '''Ganglioneuroma''' is a benign neuroblasic tumour. It is also known as '''ganglioma'''.<ref>URL: [http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma]. Accessed on: 8 November 2010.</ref> | ||
It should '''not''' to be confused with ''[[ganglioglioma]]''. | |||
==General== | |||
*May be retroperitoneal. | |||
*Occasionally found in the GI tract - may form [[Gastrointestinal_tract_polyps#Ganglioneuroma|colonic polyp]]. | |||
*Multiple ganglioneuromas may be due to [[multiple endocrine neoplasia IIb]]. | |||
Classification: | |||
*In a grouping known as ''neuroblastic tumours'' which includes:<ref name=pmid10421272>{{cite journal |author=Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J, Joshi VV, Roald B |title=Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee |journal=Cancer |volume=86 |issue=2 |pages=349–63 |year=1999 |month=July |pmid=10421272 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
**Ganglioneuroma (benign). | |||
**[[Ganglioneuroblastoma]] (intermediate). | |||
**[[Neuroblastoma]] (aggressive). | |||
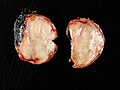
==Gross== | |||
*Solid. | |||
*White. | |||
*Firm. | |||
*Well-circumscribed. | |||
*May be nodular. | |||
===Images=== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Adrenal_ganglioneuroma_02.JPG | Adrenal ganglioneuroma. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=84&n=1 Ganglioneuroma (webpathology.com)]. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Ganglion cells - '''key feature'''. | |||
**Large cells with large nucleus. | |||
***Prominent nucleolus. | |||
*Disordered fibrinous-like material. | |||
*Eosinophilic granular bodies.<ref>R. Kiehl. 8 November 2010.</ref> | |||
See: ''[[adrenal ganglioneuroma]]'', ''[[Gastrointestinal tract polyps#Ganglioneuroma|colonic ganglioneuroma]]''. | |||
===Images=== | |||
*[http://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ganglioneuroma_(1).jpg Ganglioneuroma (WC)]. | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?n=4&Case=84 Ganglioneuroma (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.webpathology.com/image.asp?case=412&n=4 Ganglioneuroma (webpathology.com)]. | |||
*[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Ganglion_high_mag.jpg Normal ganglion - high mag. (WC)] . | |||
==IHC== | |||
Features:<ref>{{Ref GLP|217}}</ref> | |||
*Spindle cells: S-100 +ve. | |||
*Ganglion cells: NSE, synaptophysin, NF. | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Neuropathology tumours]]. | |||
==References== | |||
{{Reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | [[Category:Diagnosis]] | ||
[[Category:Neuropathology tumours]] | |||
Revision as of 07:34, 10 December 2014
Ganglioneuroma is a benign neuroblasic tumour. It is also known as ganglioma.[1]
It should not to be confused with ganglioglioma.
General
- May be retroperitoneal.
- Occasionally found in the GI tract - may form colonic polyp.
- Multiple ganglioneuromas may be due to multiple endocrine neoplasia IIb.
Classification:
- In a grouping known as neuroblastic tumours which includes:[2]
- Ganglioneuroma (benign).
- Ganglioneuroblastoma (intermediate).
- Neuroblastoma (aggressive).
Gross
- Solid.
- White.
- Firm.
- Well-circumscribed.
- May be nodular.
Images
www:
Microscopic
Features:
- Ganglion cells - key feature.
- Large cells with large nucleus.
- Prominent nucleolus.
- Large cells with large nucleus.
- Disordered fibrinous-like material.
- Eosinophilic granular bodies.[3]
See: adrenal ganglioneuroma, colonic ganglioneuroma.
Images
- Ganglioneuroma (WC).
- Ganglioneuroma (webpathology.com).
- Ganglioneuroma (webpathology.com).
- Normal ganglion - high mag. (WC) .
IHC
Features:[4]
- Spindle cells: S-100 +ve.
- Ganglion cells: NSE, synaptophysin, NF.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/ganglioma. Accessed on: 8 November 2010.
- ↑ Shimada H, Ambros IM, Dehner LP, Hata J, Joshi VV, Roald B (July 1999). "Terminology and morphologic criteria of neuroblastic tumors: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Pathology Committee". Cancer 86 (2): 349–63. PMID 10421272.
- ↑ R. Kiehl. 8 November 2010.
- ↑ Iacobuzio-Donahue, Christine A.; Montgomery, Elizabeth A. (2005). Gastrointestinal and Liver Pathology: A Volume in the Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology Series (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 217. ISBN 978-0443066573.