Difference between revisions of "Pulmonary infarct"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(touch) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
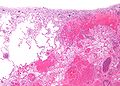
| Image = Pulmonary_infarct_intermed_mag.jpg | | Image = Pulmonary_infarct_intermed_mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Pulmonary infarct. [[H&E stain]]. | | Caption = Pulmonary infarct. [[H&E stain]]. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
| Grossing = | | Grossing = | ||
| Site = [[lung]] | | Site = [[lung]] | ||
| Assdx = underlying causes: [[sickle cell disease]], [[pulmonary embolism]], [[vasculitides]], malignancy (e.g. [[lymphoma]]), others | | Assdx = underlying causes: [[sickle cell disease]], [[pulmonary embolism]], [[vasculitides]], malignancy (e.g. [[lymphoma]]), drug toxicity, others | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = | ||
Latest revision as of 02:48, 29 March 2015
| Pulmonary infarct | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
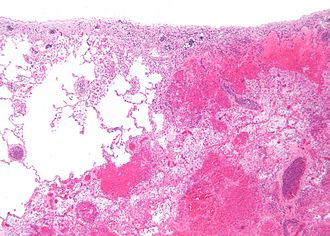 Pulmonary infarct. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | lung infarct |
|
| |
| LM | necrosis of alveolar walls - loss of nuclei, alveolar hemorrhage, +/-evidence of underlying cause |
| LM DDx | see Associated Dx |
| Gross | lung periphery, classically described as wedge-shaped |
| Site | lung |
|
| |
| Associated Dx | underlying causes: sickle cell disease, pulmonary embolism, vasculitides, malignancy (e.g. lymphoma), drug toxicity, others |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | reverse halo sign |
| Prognosis | dependent on underlying cause |
| Treatment | dependent on underlying cause |
Pulmonary infarct is the death of lung tissue due to oxygen deprivation.
It is also known as a lung infarct, lung infarction, and pulmonary infarction.
General
- Uncommon because of the dual blood supply (systemic via the bronchial arteries, pulmonary via the pulmonary arteries).
Common causes:[1]
Less common causes:
- Lymphoma, esp. acute promyelocytic leukemia.
- Drugs, e.g. chemotherapy.
- Vasculitis.
- Others.
Gross
- Lung periphery, classically described as wedge-shaped.
Note:
- In a histologic section, the classic wedge-shaped infarct is triangular:
- Base of triangle on the pleural aspect.
- Point furthest from the pleura close to the compromised artery that lead to infarction.
Radiology:
- Reverse halo sign.[2]
Images:
Microscopic
Features:
- Necrosis of alveolar walls - loss of nuclei.
- Alveolar hemorrhage.
Image
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/908045-overview. Accessed on: 12 April 2012.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Casullo, J.; Semionov, A. (Feb 2013). "Reversed halo sign in acute pulmonary embolism and infarction.". Acta Radiol. doi:10.1177/0284185113475797. PMID 23395814.