Difference between revisions of "Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| LMDDx = | | LMDDx = | ||
| Stains = | | Stains = | ||
| IHC = Langerhans cells (CD1a +ve, S-100 +ve, CD207 +ve | | IHC = Langerhans cells (CD1a +ve, S-100 +ve, CD207 +ve) | ||
| EM = | | EM = | ||
| Molecular = | | Molecular = | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| Assdx = | | Assdx = | ||
| Syndromes = | | Syndromes = | ||
| Clinicalhx = | | Clinicalhx = [[smoking|smoker]], usually male 20-40 years old | ||
| Signs = | | Signs = +/-non-productive cough | ||
| Symptoms = | | Symptoms = +/-[[dyspnea]] | ||
| Prevalence = uncommon | | Prevalence = uncommon | ||
| Bloodwork = | | Bloodwork = | ||
| Rads = upper lung zones | | Rads = peribronchial nodules, upper lung zones or mid, multiple irregular cysts | ||
| Endoscopy = | | Endoscopy = | ||
| Prognosis = good with smoking cessation | | Prognosis = good with smoking cessation | ||
| Other = | | Other = | ||
| ClinDDx = | | ClinDDx = non-pulmonary [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]] | ||
| Tx = | | Tx = | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis''' is an uncommon [[smoking|smoking-related lung disease]]. | '''Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis''' is an uncommon [[smoking|smoking-related lung disease]]. | ||
It is also known as '''eosinophilic granuloma of the lung'''. | It is also known as '''eosinophilic granuloma of the lung'''. | ||
The term ''Langerhans cell histiocytosis'' refers to several different diseases; a separate article deals with the other types of [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]]. | |||
==General== | ==General== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
*Not associated with systemic diseases of Langerhans cells ([[AKA]] [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis|Hand-Schueller-Christian disease]]). | *Not associated with systemic diseases of Langerhans cells ([[AKA]] [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis|Hand-Schueller-Christian disease]]). | ||
Clinical - features:<ref name=pmid25473537>{{Cite journal | last1 = Martin | first1 = I. | last2 = Ballester | first2 = M. | last3 = Ruiz | first3 = Y. | last4 = Llatjós | first4 = R. | last5 = Alarza | first5 = F. | last6 = Molina | first6 = M. | title = Presentation of pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis before the development of lung cysts. | journal = Respirol Case Rep | volume = 1 | issue = 2 | pages = 34-5 | month = Dec | year = 2013 | doi = 10.1002/rcr2.11 | PMID = 25473537 }}</ref> | |||
*Non-productive cough. | |||
*[[Dyspnea]]. | |||
*Typically males - 20-40 years old. | |||
*Smokers. | |||
===Subtypes=== | |||
Subtypes:<ref name=Ref_PPP234/> | Subtypes:<ref name=Ref_PPP234/> | ||
*Cellular form. | *Cellular form. | ||
*Fibrotic form. | *Fibrotic form. | ||
One form usually predominates. | Note: | ||
*One form usually predominates. | |||
==Radiology== | ==Radiology== | ||
*Upper lung zones. | *Upper lung zones. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 66: | ||
**+/-Eosinophilia (may be rare) - '''significantly narrow DDx'''. | **+/-Eosinophilia (may be rare) - '''significantly narrow DDx'''. | ||
**Chronic inflammatory cells (lymphocytes). (???) | **Chronic inflammatory cells (lymphocytes). (???) | ||
DDx: | |||
*Non-pulmonary [[Langerhans cell histiocytosis]] - LCH is also found outside of the lung. | |||
===Images=== | ===Images=== | ||
Latest revision as of 21:45, 15 April 2016
| Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
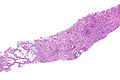
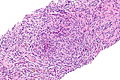
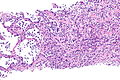
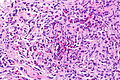
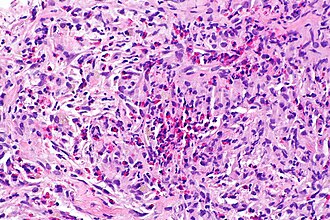 Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the lung. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| Synonyms | eosinophilic granuloma (of the lung) |
|
| |
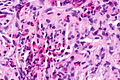
| LM | cellular peribronchiolar nodules with Langerhans cells (pale staining nucleus (H&E) with nuclear infolding - "crumpled tissue paper" appearance), +/-smoker's macrophages (brown pigmented airspace macrophages), +/-eosinophilia (typical - may be rare) |
| IHC | Langerhans cells (CD1a +ve, S-100 +ve, CD207 +ve) |
| Site | lung - see medical lung diseases |
|
| |
| Clinical history | smoker, usually male 20-40 years old |
| Signs | +/-non-productive cough |
| Symptoms | +/-dyspnea |
| Prevalence | uncommon |
| Radiology | peribronchial nodules, upper lung zones or mid, multiple irregular cysts |
| Prognosis | good with smoking cessation |
| Clin. DDx | non-pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis is an uncommon smoking-related lung disease.
It is also known as eosinophilic granuloma of the lung.
The term Langerhans cell histiocytosis refers to several different diseases; a separate article deals with the other types of Langerhans cell histiocytosis.
General
- Associated with smoking.[1]
- Not associated with systemic diseases of Langerhans cells (AKA Hand-Schueller-Christian disease).
Clinical - features:[2]
- Non-productive cough.
- Dyspnea.
- Typically males - 20-40 years old.
- Smokers.
Subtypes
Subtypes:[1]
- Cellular form.
- Fibrotic form.
Note:
- One form usually predominates.
Radiology
- Upper lung zones.
Microscopic
Features:[3]
- Cellular peribronchiolar nodules with:
- Langerhans cells - key feature:
- Pale staining nucleus (H&E) with nuclear infolding - "crumpled tissue paper" appearance.
- +/-Smoker's macrophages (brown pigmented airspace macrophages).
- +/-Eosinophilia (may be rare) - significantly narrow DDx.
- Chronic inflammatory cells (lymphocytes). (???)
- Langerhans cells - key feature:
DDx:
- Non-pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis - LCH is also found outside of the lung.
Images
www:
IHC
Langerhans cells:
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Leslie, Kevin O.; Wick, Mark R. (2004). Practical Pulmonary Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 234. ISBN 978-0443066313.
- ↑ Martin, I.; Ballester, M.; Ruiz, Y.; Llatjós, R.; Alarza, F.; Molina, M. (Dec 2013). "Presentation of pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis before the development of lung cysts.". Respirol Case Rep 1 (2): 34-5. doi:10.1002/rcr2.11. PMID 25473537.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Leslie, Kevin O.; Wick, Mark R. (2004). Practical Pulmonary Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach (1st ed.). Churchill Livingstone. pp. 237. ISBN 978-0443066313.