Difference between revisions of "Esophagus"
(→Microscopic: more) |
m (fix sp) |
||
| (209 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Esophagus''' connects the pharynx to the [[stomach]]. It is afflicted by tumours on occasion. | [[Image:Tractus intestinalis esophagus.svg|thumb|250px|A schematic of the esophagus.]] | ||
'''Esophagus''' connects the pharynx to the [[stomach]]. It is afflicted by tumours on occasion. Probably the most common affliction is [[gastroesophageal reflux disease]] (GERD). Most biopsies revolve around the questions: 1. intestinal metaplasia? 2. dysplasia? and 3. cancer? | |||
=Normal= | =Normal esophagus= | ||
General: | General: | ||
*Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium. | *Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 12: | ||
**Mitoses should be rare and should NOT be above the basal layer. | **Mitoses should be rare and should NOT be above the basal layer. | ||
*Inflammatory cells should be very rare. | *Inflammatory cells should be very rare. | ||
==Sign out== | |||
===Nonspecific inflammation=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Esophagus, Distal, Biopsy: | |||
- Columnar epithelium with moderate chronic inflammation. | |||
- Reactive squamous epithelium. | |||
- NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia. | |||
- NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy. | |||
</pre> | |||
====Block letters==== | |||
<pre> | |||
ESOPHAGUS, DISTAL, BIOPSY: | |||
- COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH MODERATE CHRONIC INFLAMMATION. | |||
- REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY. | |||
</pre> | |||
=Diagnoses= | =Diagnoses= | ||
| Line 26: | Line 46: | ||
==Tabular summary== | ==Tabular summary== | ||
===Simplified overview=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|'''Entity''' | |'''Entity''' | ||
| Line 39: | Line 60: | ||
| - | | - | ||
| - | | - | ||
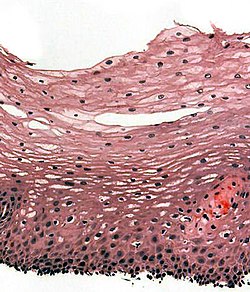
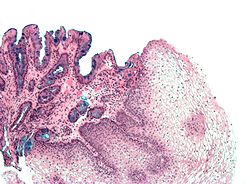
| [ | | [[Image:Tinci%C3%B3n_hematoxilina-eosina.jpg|center|thumb|125px|Normal esophagus. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|GERD | |GERD | ||
| Line 46: | Line 67: | ||
| | | | ||
| incr. risk of Barrett's | | incr. risk of Barrett's | ||
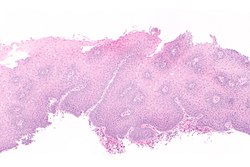
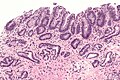
| | | [[Image:Gastroesophageal reflux disease -- low mag.jpg|center|thumb|125px|c/w GERD. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Eosinophilic esophagitis | |[[Eosinophilic esophagitis]] | ||
| abundant eosinophils | | abundant eosinophils | ||
| elongated (epithelial) papillae, basal cell hyperplasia, lymphocytes | | elongated (epithelial) papillae, basal cell hyperplasia, lymphocytes | ||
| | | | ||
| unresponsive to PPIs | | unresponsive to PPIs | ||
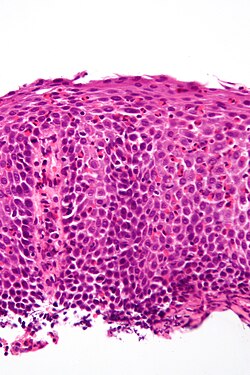
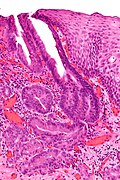
| [ | | [[Image:Eosinophilic_esophagitis_-_2_-_very_high_mag.jpg|center|thumb|125px|Eosinophilic esophagitis. (WC/Nephron)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Barrett's type change | |[[Barrett's esophagus|Barrett's type change]] | ||
| goblet cells | | goblet cells | ||
| no dysplasia | | no dysplasia | ||
| Alcian blue +ve | | Alcian blue +ve | ||
| incr. risk of adenocarcinoma | | incr. risk of adenocarcinoma | ||
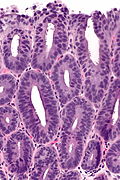
| [ | | [[Image:Barretts_alcian_blue.jpg|center|thumb|125px|Barrett's esophagus. Alcian blue. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Dysplasia, low grade | |[[Columnar dysplasia of the esophagus|Dysplasia, low grade]] | ||
| nuclear crowding at surface | | nuclear crowding at surface | ||
| hyperchromasia, mild arch. complexity | | hyperchromasia, mild arch. complexity, no necrosis | ||
| | | | ||
| incr. risk of carcinoma | | incr. risk of carcinoma | ||
| | | [[Image:Low-grade columnar dysplasia of the esophagus -- intermed mag.jpg|thumb|110px|LGH - intermed. mag.]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Dysplasia, high grade | | [[Columnar dysplasia of the esophagus|Dysplasia, high grade]] | ||
| | | [[cribriform]]ing and/or necrosis | ||
| | | nuclei often round & large, hyperchromasia | ||
| | | | ||
| marked incr. risk of carcinoma | | marked incr. risk of carcinoma | ||
| | | [[Image:High-grade columnar dysplasia of the esophagus -- high mag.jpg|thumb|110px|HGD - high mag.]] | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
|Entity | |Entity | ||
| Line 85: | Line 106: | ||
--> | --> | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Columnar dysplasia=== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|'''Entity''' | |||
|'''Surface maturation''' | |||
|'''Architecture''' | |||
|'''Cytology''' | |||
|'''Other''' | |||
|'''Clinical''' | |||
|'''Image''' | |||
|- | |||
|Normal | |||
| '''matures''' | |||
| round glands | |||
| no nuclear atypia | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| [[Image:Tinci%C3%B3n_hematoxilina-eosina.jpg|center|thumb|125px|Normal esophagus. (WC)]] | |||
|- | |||
|Barrett's esophagus | |||
| matures | |||
| round glands, normal gland density | |||
| +/-scant nuclear atypia | |||
| '''goblet cells''' | |||
| clinical diagnosis | |||
| Image | |||
|- | |||
|Indefinite for columnar dysplasia | |||
| minimal maturation ''or'' '''cannot see surface''' | |||
| round glands, normal gland density | |||
| mild nuclear atypia, '''nuclear pseudostratification''', no necrosis | |||
| - | |||
| follow-up | |||
| Image | |||
|- | |||
|Low-grade columnar dysplasia | |||
| minimal-to-scant maturation | |||
| round glands, +/-rare budding, increased gland density | |||
| mild-to-moderate nuclear atypia, '''nuclear pseudostratification''', '''no necrosis''' | |||
| - | |||
| follow-up | |||
| [[Image:Low-grade columnar dysplasia of the esophagus -- intermed mag.jpg|thumb|110px|LGH - intermed. mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
|High-grade columnar dysplasia | |||
| no maturation | |||
| '''incr. density of irregular glands''' with budding and/or rare cribriforming and/or gland dilation | |||
| moderate-to-marked nuclear atypia (usu. plump round nuclei), hyperchromasia, +/-necrosis | |||
| - | |||
| [[EMR]], surgery | |||
| [[Image:High-grade columnar dysplasia of the esophagus -- high mag.jpg|thumb|110px|HGD - high mag.]] | |||
|- | |||
|Intramucosal adenocarcinoma | |||
| no maturation | |||
| single cells or '''back-to-back irregular glands''' with budding and/or '''[[cribriform]]ing''' and/or '''gland dilation''' or glands with long axis along muscularis mucosae | |||
| moderate-to-marked nuclear atypia - usu. round large nuclei, hyperchromasia, +/-necrosis | |||
| - | |||
| [[EMR]], surgery | |||
| [[Image:Esophageal_adenocarcinoma_-_high_mag.jpg|thumb|110px|Adenocarcinoma - high mag.]] | |||
|} | |||
===Columnar dysplasia - another table=== | |||
{| class="wikitable sortable" style="margin-left:auto;margin-right:auto" | |||
!'''Feature''' | |||
!'''Indefinite for columnar dysplasia''' | |||
!'''Low-grade columnar dysplasia''' | |||
!'''High-grade columnar dysplasia''' | |||
!'''Intramucosal carcinoma (IMCa)''' | |||
!'''Utility''' | |||
|- | |||
| Depth of glands | |||
| superficial only | |||
| superficial only | |||
| superficial/deep | |||
| deep | |||
| low vs. high | |||
|- | |||
| Gland density | |||
| normal | |||
| near normal | |||
| increased | |||
| back-to-back | |||
| low vs. high vs. IMCa | |||
|- | |||
| Gland morphology | |||
| round | |||
| round | |||
| irregular/rare cribriforming | |||
| irregular/cribriform/sheeting | |||
| low vs. high vs. IMCa | |||
|- | |||
| Necrosis | |||
| none | |||
| none | |||
| may be present | |||
| may be present | |||
| low vs. high & IMCa | |||
|- | |||
| Hyperchromasia | |||
| +/- | |||
| present | |||
| present | |||
| present | |||
| indef. vs. low | |||
|- | |||
| Palisaded/crowded nuclei | |||
| present | |||
| present | |||
| absent/present | |||
| uncommon | |||
| low vs. high | |||
|- | |||
| Round nuclei + enlargement | |||
| absent | |||
| absent | |||
| present/absent | |||
| present | |||
| low vs. high | |||
|- | |||
| [[Desmoplasia]] | |||
| absent | |||
| absent | |||
| absent | |||
| +/- (uncommon) | |||
| high vs. IMCa | |||
|- | |||
| Surface involvement | |||
| present (required) | |||
| present (required) | |||
| +/- | |||
| +/- | |||
| low vs. high | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
====Decision tree for columnar dysplasia==== | |||
Odze has made an algorithm - see: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1861756/figure/fig8/ Diagnostic algorithm (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid17021130>{{Cite journal | last1 = Odze | first1 = RD. | title = Diagnosis and grading of dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus. | journal = J Clin Pathol | volume = 59 | issue = 10 | pages = 1029-38 | month = Oct | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1136/jcp.2005.035337 | PMID = 17021130 }}</ref> | |||
==Indications== | ==Indications== | ||
*Pyrosis = heartburn.<ref>URL: [http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pyrosis http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pyrosis]. Accessed on: 21 June 2010.</ref> | *Pyrosis = heartburn.<ref>URL: [http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pyrosis http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pyrosis]. Accessed on: 21 June 2010.</ref> | ||
= | =Infectious esophagitis= | ||
{{main|Microorganisms}} | {{main|Microorganisms}} | ||
Is a relatively common problem, especially in those that live at the margins (EtOH abusers) and immunosuppressed individuals ([[HIV|HIV/AIDS]]). | Is a relatively common problem, especially in those that live at the margins (EtOH abusers) and immunosuppressed individuals ([[HIV|HIV/AIDS]]). | ||
| Line 103: | Line 260: | ||
*[[HIV]] - non-specific. | *[[HIV]] - non-specific. | ||
=== | ===Candida esophagitis=== | ||
{{Main|Candidiasis}} | |||
*[[AKA]] ''esophageal candidiasis''. | |||
====Gross (endoscopic)==== | ====Gross (endoscopic)==== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*White patches. | *White patches. | ||
DDx (endoscopic):<ref name=Ref_Odze244>{{Ref Odze|244}}</ref> | |||
*[[Eosinophilic esophagitis]]. | |||
====Microscopic==== | ====Microscopic==== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Worm-like micro-organisms. | *Worm-like micro-organisms - '''key feature'''. | ||
**Pseudohyphae (single cells). | **Pseudohyphae (single cells). | ||
**Thickness ~ 1/3-1/2 of squamous cell nucleus. | **Thickness ~ 1/3-1/2 of squamous cell nucleus. | ||
**Should be within (squamous) epithelium. | **Should be within (squamous) epithelium. | ||
* | *Superficial inflammation - esp. [[neutrophils]] - '''important'''. | ||
Notes: | |||
*On top of epithelium does not count,<ref>ALS. 4 October 2010.</ref> i.e. it is likely an artifact. | |||
*Bacilli and cocci may accompany the candida. They are typically ignored. | |||
=== | DDx: | ||
*[[Acute esophagitis]] - no candida seen. | |||
=====Image===== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Esophageal_candidiasis_(2)_PAS_stain.jpg | Esophageal candidiasis. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
====Sign out==== | |||
<pre> | |||
ESOPHAGUS, BIOPSY: | |||
- ESOPHAGITIS WITH FUNGAL ORGANISMS CONSISTENT WITH CANDIDA. | |||
</pre> | |||
<pre> | |||
ESOPHAGUS, BIOPSY: | |||
- ACUTE ESOPHAGITIS WITH FUNGAL ORGANISMS CONSISTENT WITH CANDIDA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. | |||
- NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA. | |||
</pre> | |||
=== | ===Cytomegalovirus esophagitis=== | ||
*[[AKA]] [[CMV]] esophagitis. | |||
*[[ | |||
====Microscopic==== | ====Microscopic==== | ||
Features | Features: | ||
*''' | *Classically at the base of the ulcer; within endothelial cells - '''key point'''. | ||
* | Note: | ||
*Biopsying the the base of an ulcer usually just yields (non-diagnostic) necrotic debris; so, clinicians are told to biopsy the edge of the lesion. A suspected CMV infection is the exception to this rule! | |||
===Herpes esophagitis=== | |||
{{Main|Herpes esophagitis}} | |||
===Human papillomavirus esophagitis=== | ===Human papillomavirus esophagitis=== | ||
| Line 156: | Line 334: | ||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Low-grade_sil_and_endocx.jpg LSIL & endocervix (WC)]. | *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Low-grade_sil_and_endocx.jpg LSIL & endocervix (WC)]. | ||
= | =Non-neoplastic disease= | ||
The group of conditions doesn't fit neatly with the others. It is a mixture of different non-neoplastic conditions. | |||
==Gastroesophageal reflux disease== | ==Gastroesophageal reflux disease== | ||
*Abbreviated ''GERD'' or ''GORD'' (gastro-oesophageal reflux disease). | |||
*Abbreviated ''GERD'' | *[[AKA]] ''reflux esophagitis''. | ||
{{Main|Gastroesophageal reflux disease}} | |||
* | |||
==Eosinophilic esophagitis== | ==Eosinophilic esophagitis== | ||
*Abbreviated ''EE''. | |||
{{Main|Eosinophilic esophagitis}} | |||
*''' | |||
==Erosive esophagitis== | ==Erosive esophagitis== | ||
| Line 245: | Line 358: | ||
===Pill esophagitis=== | ===Pill esophagitis=== | ||
Classic causes: | Classic causes: | ||
*Alendronate (Fosamax) - for osteoporosis. | *Alendronate (Fosamax) - for [[osteoporosis]]. | ||
*Iron | *Iron - can be demonstrated with [[Prussian blue stain]]. | ||
*Doxycycline. | *Doxycycline. | ||
==Esophageal varices== | |||
{{Main|Esophageal varices}} | |||
==Acute esophagitis== | |||
{{Main|Acute esophagitis}} | |||
==Benign esophageal stricture== | |||
{{Main|Esophageal stricture}} | |||
==Esophageal duplication cyst== | |||
{{Main|Foregut duplication cyst}} | |||
==Zenker's diverticulum== | |||
{{Main|Zenker's diverticulum}} | |||
*[[AKA]] ''cricopharyngeal diverticulum'', ''pharyngoesophageal diverticulum'' and ''hypopharyngeal diverticulum''. | |||
==Radiation esophagitis== | |||
{{Main|Radiation esophagitis}} | |||
=Preneoplastic= | =Preneoplastic= | ||
==Barrett's esophagus== | ==Barrett esophagus== | ||
{{Main|Barrett esophagus}} | |||
=Neoplastic= | |||
==Columnar dysplasia of the esophagus== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''esophageal columnar dysplasia'', abbreviated ''ECD''.<ref name=pmid21809994>{{Cite journal | last1 = Feng | first1 = W. | last2 = Zhou | first2 = Z. | last3 = Peters | first3 = JH. | last4 = Khoury | first4 = T. | last5 = Zhai | first5 = Q. | last6 = Wei | first6 = Q. | last7 = Truong | first7 = CD. | last8 = Song | first8 = SW. | last9 = Tan | first9 = D. | title = Expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 in human esophageal adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions. | journal = Arch Pathol Lab Med | volume = 135 | issue = 8 | pages = 1024-31 | month = Aug | year = 2011 | doi = 10.5858/2009-0617-OAR2 | PMID = 21809994 }}</ref> | |||
*[[AKA]] ''dysplasia in the columnar-lined esophagus''.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Levine | first1 = DS. | title = Management of dysplasia in the columnar-lined esophagus. | journal = Gastroenterol Clin North Am | volume = 26 | issue = 3 | pages = 613-34 | month = Sep | year = 1997 | doi = | PMID = 9309409 }}</ref> | |||
* [[AKA]] ''columnar epithelial dysplasia''.<ref name=pmid3825997>{{Cite journal | last1 = Hamilton | first1 = SR. | last2 = Smith | first2 = RR. | title = The relationship between columnar epithelial dysplasia and invasive adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's esophagus. | journal = Am J Clin Pathol | volume = 87 | issue = 3 | pages = 301-12 | month = Mar | year = 1987 | doi = | PMID = 3825997 }}</ref> | |||
{{Main|Columnar dysplasia of the esophagus}} | |||
==Squamous dysplasia of the esophagus== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''esophageal squamous dysplasia''. | |||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
* | *Precursor of [[esophageal squamous cell carcinoma]].<ref name=pmid11936262>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dry | first1 = SM. | last2 = Lewin | first2 = KJ. | title = Esophageal squamous dysplasia. | journal = Semin Diagn Pathol | volume = 19 | issue = 1 | pages = 2-11 | month = Feb | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 11936262 }}</ref> | ||
*Common in China.<ref name=pmid11936262/> | |||
*Not very common in North America. | |||
==== | |||
* | |||
* | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Squamous cell nuclear atypia. | ||
* | *Lack of maturation to the surface. | ||
Images: | Note: | ||
*[http:// | *Grading differences between Western pathologists and those of the east.<ref name=pmid11936262/> | ||
DDx: | |||
*Reactive changes. | |||
*[[Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma]]. | |||
====Images==== | |||
A set of cases from Japan:<ref name=pmid23330004>{{Cite journal | last1 = Terada | first1 = T. | title = A clinicopathologic study of esophageal 860 benign and malignant lesions in 910 cases of consecutive esophageal biopsies. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 6 | issue = 2 | pages = 191-8 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = | PMID = 23330004 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544238/figure/fig05/ Mild squamous dysplasia (nih.gov)]. | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544238/figure/fig06/ Moderate squamous dysplasia (nih.gov)]. | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544238/figure/fig07/ Severe squamous dysplasia (nih.gov)]. | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544238/figure/fig08/ Carcinoma in situ (nih.gov)]. | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544238/figure/fig09/ Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (nih.gov)]. | |||
= | ===IHC=== | ||
== | *Ki-67 may be useful:<ref name=pmid21420715>{{Cite journal | last1 = Wang | first1 = WC. | last2 = Wu | first2 = TT. | last3 = Chandan | first3 = VS. | last4 = Lohse | first4 = CM. | last5 = Zhang | first5 = L. | title = Ki-67 and ProExC are useful immunohistochemical markers in esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 42 | issue = 10 | pages = 1430-7 | month = Oct | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.12.009 | PMID = 21420715 }}</ref> | ||
=== | **Reactive changes/normal: ~98% negative, ~2% intermediate. | ||
* | **Low-grade esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (LGESIN): ~80% intermediate, ~20% negative. | ||
** | **High-grade esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (HGESIN): ~37% intermediate, ~63% strong. | ||
* | |||
*High grade | |||
=== | Definitions:<ref name=pmid21420715/> | ||
*Negative defined as: < 25% of epithelium +ve ''and'' staining only in lower quarter of epithelium. | |||
* | *Intermediate defined: >=25% and <=50% of epithelium +ve ''and'' only in the lower half of the epithelium. | ||
*Strong defined: >50% of epithelium +ve ''or'' upper half of epithelium. | |||
==Leiomyoma of the esophagus== | |||
{{Main|Leiomyoma}} | |||
* | ===General=== | ||
*Benign. | |||
*Uncommon. | |||
**Before the time of [[GIST]]s - this was a relatively common diagnosis. | |||
*Like [[leiomyoma]]s elswhere. | |||
===Microscopic=== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
:''See: [[Leiomyoma]]''. | |||
DDx: | |||
* | *[[Gastrointestinal stromal tumour]]. | ||
* | *[[Schwannoma]]. | ||
==Gastrointestinal stromal tumour== | |||
{{Main|Gastrointestinal stromal tumour}} | |||
=[[Cancer]]= | =[[Cancer]]= | ||
| Line 314: | Line 458: | ||
*[[Smoking]]. | *[[Smoking]]. | ||
==Squamous cell carcinoma== | ==Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus== | ||
{{Main|Squamous | *[[AKA]] ''esophageal squamous cell carcinoma'', abbreviated ''esophageal SCC''. | ||
{{Main|Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus}} | |||
== | ==Esophageal adenocarcinoma== | ||
*[[AKA]] ''adenocarcinoma of the esophagus''. | |||
{{Main|Esophageal adenocarcinoma}} | |||
=Weird stuff= | =Weird stuff= | ||
| Line 361: | Line 471: | ||
*Granular cell tumour. | *Granular cell tumour. | ||
*Squamous papilloma - koilocytes. | *Squamous papilloma - koilocytes. | ||
*Heterotopic gastric mucosa ("inlet patch") - benign appearing gastric mucosa. | *Heterotopic gastric mucosa ("[[inlet patch]]") - benign appearing gastric mucosa. | ||
==Granular cell tumour== | ==Granular cell tumour== | ||
| Line 374: | Line 484: | ||
*Usu. bland (cytologically non-malignant) nuclei. | *Usu. bland (cytologically non-malignant) nuclei. | ||
Images: | ====Images==== | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3544238/figure/fig04/ GCT of the esophagus (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid23330004>{{Cite journal | last1 = Terada | first1 = T. | title = A clinicopathologic study of esophageal 860 benign and malignant lesions in 910 cases of consecutive esophageal biopsies. | journal = Int J Clin Exp Pathol | volume = 6 | issue = 2 | pages = 191-8 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = | PMID = 23330004 }}</ref> | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granular_cell_tumor_(3)_skin.jpg GCT - skin (WC)]. | *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granular_cell_tumor_(3)_skin.jpg GCT - skin (WC)]. | ||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granular_cell_tumor_(4)_S-100.JPG GCT - S100 (WC)]. | *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Granular_cell_tumor_(4)_S-100.JPG GCT - S100 (WC)]. | ||
| Line 382: | Line 493: | ||
===General=== | ===General=== | ||
*Rare & benign condition that resolves without | *Rare & benign condition that resolves without lasting pathology.<ref name=pmid19809273/> | ||
**Case report - chronic with strictures.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Coppola | first1 = D. | last2 = Lu | first2 = L. | last3 = Boyce | first3 = HW. | title = Chronic esophagitis dissecans presenting with esophageal strictures: a case report. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 10 | pages = 1313-7 | month = Oct | year = 2000 | doi = 10.1053/hupa.2000.18470 | PMID = 11070124 }} | **Case report - chronic with strictures.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Coppola | first1 = D. | last2 = Lu | first2 = L. | last3 = Boyce | first3 = HW. | title = Chronic esophagitis dissecans presenting with esophageal strictures: a case report. | journal = Hum Pathol | volume = 31 | issue = 10 | pages = 1313-7 | month = Oct | year = 2000 | doi = 10.1053/hupa.2000.18470 | PMID = 11070124 }} | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
| Line 393: | Line 504: | ||
*Parakeratosis. | *Parakeratosis. | ||
*Variable acute or chronic inflammation. | *Variable acute or chronic inflammation. | ||
==Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus== | |||
{{Main|Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus}} | |||
==Achalasia== | |||
{{main|Achalasia}} | |||
==Esophageal inlet patch== | |||
*[[AKA]] ''inlet patch'', [[AKA]] ''cervical inlet patch''. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Benign and likely not of any significance.<ref name=pmid23372354/> | |||
===Gross=== | |||
*Proximal esophagus - salmon coloured lesion.<ref name=pmid23372354>{{Cite journal | last1 = Chong | first1 = VH. | title = Clinical significance of heterotopic gastric mucosal patch of the proximal esophagus. | journal = World J Gastroenterol | volume = 19 | issue = 3 | pages = 331-8 | month = Jan | year = 2013 | doi = 10.3748/wjg.v19.i3.331 | PMID = 23372354 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Gastric mucosa.<ref name=pmid22091379/> | |||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3197178/figure/fig4/ Esophageal inlet patch (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid22091379>{{Cite journal | last1 = Behrens | first1 = C. | last2 = Yen | first2 = PP. | title = Esophageal inlet patch. | journal = Radiol Res Pract | volume = 2011 | issue = | pages = 460890 | month = | year = 2011 | doi = 10.1155/2011/460890 | PMID = 22091379 }}</ref> | |||
===Sign out=== | |||
<pre> | |||
Esophagus at 22 cm, Biopsy: | |||
- Gastric type mucosa with mild chronic inactive inflammation, see comment. | |||
- Scant unremarkable squamous epithelium. | |||
- NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia. | |||
- NEGATIVE for dysplasia. | |||
Comment: | |||
This is in keeping with an "inlet patch", also known as "heterotopic gastric mucosal patch of the proximal esophagus". | |||
</pre> | |||
==Squamous papilloma of the esophagus== | |||
{{Main|Squamous papilloma of the esophagus}} | |||
=See also= | =See also= | ||
| Line 402: | Line 549: | ||
[[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | [[Category:Gastrointestinal pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Esophagus|Esophagus]] | |||
Latest revision as of 22:57, 27 January 2022
Esophagus connects the pharynx to the stomach. It is afflicted by tumours on occasion. Probably the most common affliction is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Most biopsies revolve around the questions: 1. intestinal metaplasia? 2. dysplasia? and 3. cancer?
Normal esophagus
General:
- Stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium.
Normal (esophageal) squamous epithelium:
- Should "mature" to the surface like good stratified squamous epithelium does.
- No nuclei at luminal surface.
- Cells should become less hyperchromatic as you go toward the lumen.
- Mitoses should be rare and should NOT be above the basal layer.
- Inflammatory cells should be very rare.
Sign out
Nonspecific inflammation
Esophagus, Distal, Biopsy: - Columnar epithelium with moderate chronic inflammation. - Reactive squamous epithelium. - NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia. - NEGATIVE for dysplasia and NEGATIVE for malignancy.
Block letters
ESOPHAGUS, DISTAL, BIOPSY: - COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM WITH MODERATE CHRONIC INFLAMMATION. - REACTIVE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM. - NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA AND NEGATIVE FOR MALIGNANCY.
Diagnoses
Common
- Normal.
- Metaplasia (Barrett's esophagus).
- Dysplasia.
- Adenocarcinoma.
Less common
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis.
- Candidiasis.
- CMV esophagitis.
Tabular summary
Simplified overview
| Entity | Key feature | Other features | IHC/Special | Clinical | Image |
| Normal | squamous epi. matures to surface | no inflammation, no atypia | - | - | |
| GERD | inflammation (eosinophils, lymphocytes) | elongated (epithelial) papillae, basal cell hyperplasia | incr. risk of Barrett's | ||
| Eosinophilic esophagitis | abundant eosinophils | elongated (epithelial) papillae, basal cell hyperplasia, lymphocytes | unresponsive to PPIs | ||
| Barrett's type change | goblet cells | no dysplasia | Alcian blue +ve | incr. risk of adenocarcinoma | |
| Dysplasia, low grade | nuclear crowding at surface | hyperchromasia, mild arch. complexity, no necrosis | incr. risk of carcinoma | ||
| Dysplasia, high grade | cribriforming and/or necrosis | nuclei often round & large, hyperchromasia | marked incr. risk of carcinoma |
Columnar dysplasia
| Entity | Surface maturation | Architecture | Cytology | Other | Clinical | Image |
| Normal | matures | round glands | no nuclear atypia | - | - | |
| Barrett's esophagus | matures | round glands, normal gland density | +/-scant nuclear atypia | goblet cells | clinical diagnosis | Image |
| Indefinite for columnar dysplasia | minimal maturation or cannot see surface | round glands, normal gland density | mild nuclear atypia, nuclear pseudostratification, no necrosis | - | follow-up | Image |
| Low-grade columnar dysplasia | minimal-to-scant maturation | round glands, +/-rare budding, increased gland density | mild-to-moderate nuclear atypia, nuclear pseudostratification, no necrosis | - | follow-up | |
| High-grade columnar dysplasia | no maturation | incr. density of irregular glands with budding and/or rare cribriforming and/or gland dilation | moderate-to-marked nuclear atypia (usu. plump round nuclei), hyperchromasia, +/-necrosis | - | EMR, surgery | |
| Intramucosal adenocarcinoma | no maturation | single cells or back-to-back irregular glands with budding and/or cribriforming and/or gland dilation or glands with long axis along muscularis mucosae | moderate-to-marked nuclear atypia - usu. round large nuclei, hyperchromasia, +/-necrosis | - | EMR, surgery |
Columnar dysplasia - another table
| Feature | Indefinite for columnar dysplasia | Low-grade columnar dysplasia | High-grade columnar dysplasia | Intramucosal carcinoma (IMCa) | Utility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth of glands | superficial only | superficial only | superficial/deep | deep | low vs. high |
| Gland density | normal | near normal | increased | back-to-back | low vs. high vs. IMCa |
| Gland morphology | round | round | irregular/rare cribriforming | irregular/cribriform/sheeting | low vs. high vs. IMCa |
| Necrosis | none | none | may be present | may be present | low vs. high & IMCa |
| Hyperchromasia | +/- | present | present | present | indef. vs. low |
| Palisaded/crowded nuclei | present | present | absent/present | uncommon | low vs. high |
| Round nuclei + enlargement | absent | absent | present/absent | present | low vs. high |
| Desmoplasia | absent | absent | absent | +/- (uncommon) | high vs. IMCa |
| Surface involvement | present (required) | present (required) | +/- | +/- | low vs. high |
Decision tree for columnar dysplasia
Odze has made an algorithm - see: Diagnostic algorithm (nih.gov).[1]
Indications
- Pyrosis = heartburn.[2]
Infectious esophagitis
Is a relatively common problem, especially in those that live at the margins (EtOH abusers) and immunosuppressed individuals (HIV/AIDS).
Useful stains
- PAS.
- Gram stain.
Overview
Candida esophagitis
- AKA esophageal candidiasis.
Gross (endoscopic)
Features:
- White patches.
DDx (endoscopic):[3]
Microscopic
Features:
- Worm-like micro-organisms - key feature.
- Pseudohyphae (single cells).
- Thickness ~ 1/3-1/2 of squamous cell nucleus.
- Should be within (squamous) epithelium.
- Superficial inflammation - esp. neutrophils - important.
Notes:
- On top of epithelium does not count,[4] i.e. it is likely an artifact.
- Bacilli and cocci may accompany the candida. They are typically ignored.
DDx:
- Acute esophagitis - no candida seen.
Image
Sign out
ESOPHAGUS, BIOPSY: - ESOPHAGITIS WITH FUNGAL ORGANISMS CONSISTENT WITH CANDIDA.
ESOPHAGUS, BIOPSY: - ACUTE ESOPHAGITIS WITH FUNGAL ORGANISMS CONSISTENT WITH CANDIDA. - NEGATIVE FOR INTESTINAL METAPLASIA. - NEGATIVE FOR DYSPLASIA.
Cytomegalovirus esophagitis
Microscopic
Features:
- Classically at the base of the ulcer; within endothelial cells - key point.
Note:
- Biopsying the the base of an ulcer usually just yields (non-diagnostic) necrotic debris; so, clinicians are told to biopsy the edge of the lesion. A suspected CMV infection is the exception to this rule!
Herpes esophagitis
Human papillomavirus esophagitis
General:
Microscopic
Features:
- Koilocytes:
- Perinuclear clearing.
- Nuclear changes.
- Size similar (or larger) to those in the basal layer of the epithelium.
- Nuclear enlargement should be evident on low power, i.e. 25x. [7]
- Central location - nucleus should be smack in the middle of the cell.
Images:
Non-neoplastic disease
The group of conditions doesn't fit neatly with the others. It is a mixture of different non-neoplastic conditions.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Abbreviated GERD or GORD (gastro-oesophageal reflux disease).
- AKA reflux esophagitis.
Eosinophilic esophagitis
- Abbreviated EE.
Erosive esophagitis
DDx
- Infections.
- Crohn's disease.
- Pill esophagitis.
Work-up
Pill esophagitis
Classic causes:
- Alendronate (Fosamax) - for osteoporosis.
- Iron - can be demonstrated with Prussian blue stain.
- Doxycycline.
Esophageal varices
Acute esophagitis
Benign esophageal stricture
Esophageal duplication cyst
Zenker's diverticulum
- AKA cricopharyngeal diverticulum, pharyngoesophageal diverticulum and hypopharyngeal diverticulum.
Radiation esophagitis
Preneoplastic
Barrett esophagus
Neoplastic
Columnar dysplasia of the esophagus
- AKA esophageal columnar dysplasia, abbreviated ECD.[5]
- AKA dysplasia in the columnar-lined esophagus.[6]
- AKA columnar epithelial dysplasia.[7]
Squamous dysplasia of the esophagus
- AKA esophageal squamous dysplasia.
General
- Precursor of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.[8]
- Common in China.[8]
- Not very common in North America.
Microscopic
Features:
- Squamous cell nuclear atypia.
- Lack of maturation to the surface.
Note:
- Grading differences between Western pathologists and those of the east.[8]
DDx:
- Reactive changes.
- Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Images
A set of cases from Japan:[9]
- Mild squamous dysplasia (nih.gov).
- Moderate squamous dysplasia (nih.gov).
- Severe squamous dysplasia (nih.gov).
- Carcinoma in situ (nih.gov).
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus (nih.gov).
IHC
- Ki-67 may be useful:[10]
- Reactive changes/normal: ~98% negative, ~2% intermediate.
- Low-grade esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (LGESIN): ~80% intermediate, ~20% negative.
- High-grade esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia (HGESIN): ~37% intermediate, ~63% strong.
Definitions:[10]
- Negative defined as: < 25% of epithelium +ve and staining only in lower quarter of epithelium.
- Intermediate defined: >=25% and <=50% of epithelium +ve and only in the lower half of the epithelium.
- Strong defined: >50% of epithelium +ve or upper half of epithelium.
Leiomyoma of the esophagus
General
- Benign.
- Uncommon.
- Before the time of GISTs - this was a relatively common diagnosis.
- Like leiomyomas elswhere.
Microscopic
- See: Leiomyoma.
DDx:
Gastrointestinal stromal tumour
Cancer
General
- Proximal esophagus: squamous cell carcinoma.
- Distal esophagus: adenocarcinoma arising from Barrett's esophagus.
Risks:
Squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus
- AKA esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, abbreviated esophageal SCC.
Esophageal adenocarcinoma
- AKA adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
Weird stuff
- Inflammatory polyp - assoc. trauma/previous intervention.
- Giant fibrovascular polyp - loose connective tissue covered with squamous epithelium.
- Granular cell tumour.
- Squamous papilloma - koilocytes.
- Heterotopic gastric mucosa ("inlet patch") - benign appearing gastric mucosa.
Granular cell tumour
Microscopic
Features:
- Abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm key feature.
- Granules:
- Size: 1-3 micrometers.
- Poorly demarcated.
- Granules:
- Usu. bland (cytologically non-malignant) nuclei.
Images
Esophagitis dissecans superficials
General
- Rare & benign condition that resolves without lasting pathology.[11]
- Case report - chronic with strictures.[12]
- Sloughing of large fragments of the esophageal mucosa - seen on endoscopy.
Microscopic
Features:[11]
- Flaking of superficial squamous epithelium.
- Focal bullous separation of the layers.
- Parakeratosis.
- Variable acute or chronic inflammation.
Glycogenic acanthosis of the esophagus
Achalasia
Esophageal inlet patch
General
- Benign and likely not of any significance.[13]
Gross
- Proximal esophagus - salmon coloured lesion.[13]
Microscopic
Features:
- Gastric mucosa.[14]
Image:
Sign out
Esophagus at 22 cm, Biopsy:
- Gastric type mucosa with mild chronic inactive inflammation, see comment.
- Scant unremarkable squamous epithelium.
- NEGATIVE for intestinal metaplasia.
- NEGATIVE for dysplasia.
Comment:
This is in keeping with an "inlet patch", also known as "heterotopic gastric mucosal patch of the proximal esophagus".
Squamous papilloma of the esophagus
See also
References
- ↑ Odze, RD. (Oct 2006). "Diagnosis and grading of dysplasia in Barrett's oesophagus.". J Clin Pathol 59 (10): 1029-38. doi:10.1136/jcp.2005.035337. PMID 17021130.
- ↑ URL: http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pyrosis. Accessed on: 21 June 2010.
- ↑ Odze, Robert D.; Goldblum, John R. (2009). Surgical pathology of the GI tract, liver, biliary tract and pancreas (2nd ed.). Saunders. pp. 244. ISBN 978-1416040590.
- ↑ ALS. 4 October 2010.
- ↑ Feng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Peters, JH.; Khoury, T.; Zhai, Q.; Wei, Q.; Truong, CD.; Song, SW. et al. (Aug 2011). "Expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 in human esophageal adenocarcinoma and its precursor lesions.". Arch Pathol Lab Med 135 (8): 1024-31. doi:10.5858/2009-0617-OAR2. PMID 21809994.
- ↑ Levine, DS. (Sep 1997). "Management of dysplasia in the columnar-lined esophagus.". Gastroenterol Clin North Am 26 (3): 613-34. PMID 9309409.
- ↑ Hamilton, SR.; Smith, RR. (Mar 1987). "The relationship between columnar epithelial dysplasia and invasive adenocarcinoma arising in Barrett's esophagus.". Am J Clin Pathol 87 (3): 301-12. PMID 3825997.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Dry, SM.; Lewin, KJ. (Feb 2002). "Esophageal squamous dysplasia.". Semin Diagn Pathol 19 (1): 2-11. PMID 11936262.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Terada, T. (2013). "A clinicopathologic study of esophageal 860 benign and malignant lesions in 910 cases of consecutive esophageal biopsies.". Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6 (2): 191-8. PMID 23330004.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Wang, WC.; Wu, TT.; Chandan, VS.; Lohse, CM.; Zhang, L. (Oct 2011). "Ki-67 and ProExC are useful immunohistochemical markers in esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia.". Hum Pathol 42 (10): 1430-7. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2010.12.009. PMID 21420715.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Carmack, SW.; Vemulapalli, R.; Spechler, SJ.; Genta, RM. (Dec 2009). "Esophagitis dissecans superficialis ("sloughing esophagitis"): a clinicopathologic study of 12 cases.". Am J Surg Pathol 33 (12): 1789-94. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181b7ce21. PMID 19809273.
- ↑ Coppola, D.; Lu, L.; Boyce, HW. (Oct 2000). "Chronic esophagitis dissecans presenting with esophageal strictures: a case report.". Hum Pathol 31 (10): 1313-7. doi:10.1053/hupa.2000.18470. PMID 11070124.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Chong, VH. (Jan 2013). "Clinical significance of heterotopic gastric mucosal patch of the proximal esophagus.". World J Gastroenterol 19 (3): 331-8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i3.331. PMID 23372354.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 Behrens, C.; Yen, PP. (2011). "Esophageal inlet patch.". Radiol Res Pract 2011: 460890. doi:10.1155/2011/460890. PMID 22091379.