Difference between revisions of "Microorganisms"
m (ref wmsp) |
|||
| (101 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Microorganisms''' show-up every once in a while. It is essential to know 'em. | '''Microorganisms''' show-up every once in a while. It is essential to know 'em. | ||
== | =Microorganisms= | ||
==Fungi== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
! Name (disease) | ! Name (disease) | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
! Image | ! Image | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Aspergillus (aspergillosis) | | Aspergillus ([[aspergillosis]]) | ||
| Fungi | | Fungi | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
| Fruiting heads when aerobic | | Fruiting heads when aerobic | ||
| ? Immunosuppression | | ? Immunosuppression | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref> | ||
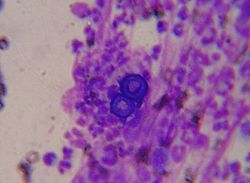
| [ | | [[Image:Pulmonary_aspergillosis.jpg|thumb|center|150px| Aspergillus. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Zygomycota (zygomycosis);<br>''more specific''<br>Mucorales (mucormycosis) | | Zygomycota ([[zygomycosis]]);<br>''more specific''<br>Mucorales (mucormycosis) | ||
| Fungi | | Fungi | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| '''Branching hyphae with variable width''' | | '''Branching hyphae with variable width''' | ||
| ? | | ? | ||
| Granulomata assoc. | | [[Granulomata]] assoc. | ||
| Diabetes, immunodeficient | | Diabetes, immunodeficient | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref> | ||
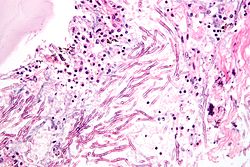
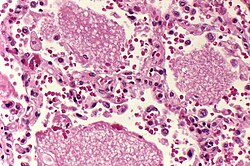
| [ | | [[Image:Zygomycosis.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Zygomycosis. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
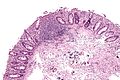
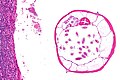
| Coccidioides, usually C. immitis<br>(coccidioidomycosis) | | Coccidioides, usually C. immitis<br>(coccidioidomycosis) | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
| Other? | | Other? | ||
| Immunodeficient | | Immunodeficient | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref> | ||
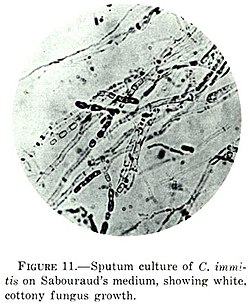
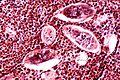
| [http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mycology/cocc3.jpg Coccidioidomycosis (med.sc.edu)] [ | | [http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mycology/cocc3.jpg Coccidioidomycosis (med.sc.edu)] [[Image:Coccidioides_immitis_on_Sabouraud%27s_medium.jpg |thumb|center|150px|C. immitis (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
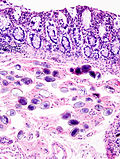
| Histoplasma (histoplasmosis) | | Histoplasma ([[histoplasmosis]]) | ||
| Fungi | | Fungi | ||
| 2-5 micrometers | | 2-5 micrometers | ||
| Spherical | | Spherical | ||
| GMS | | [[GMS]] | ||
| '''Intracellular (unlike candida), granulomata''' | | '''Intracellular (unlike candida), granulomata''' | ||
| Source: soil with bird droppings | | Source: soil with bird droppings | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref> | ||
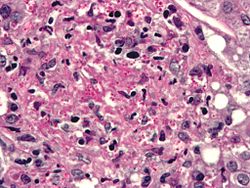
| [ | | [[Image:Histoplasma_pas-d.jpg|thumb|center|150px| Histoplasmosis. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Blastomyces ( | | Blastomyces ([[blastomycosis]]) | ||
| Fungi | | Fungi | ||
| 5-15 micrometres | | 5-15 micrometres | ||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
| Granulomas, '''broad-based budding yeast''' | | Granulomas, '''broad-based budding yeast''' | ||
| Habitat: Northeast America, Africa | | Habitat: Northeast America, Africa | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref><ref>[http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mycology/mycology-6.htm http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mycology/mycology-6.htm]</ref> | ||
| [ | | [[Image:Blastomycosis_cropped.JPG | thumb|center|150px|Blastomyces. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
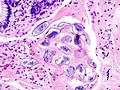
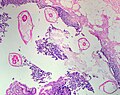
| Paracoccidioides ( | | Paracoccidioides ([[paracoccidioidomycosis]]) | ||
| Fungi | | Fungi | ||
| 6-60 micrometres | | 6-60 micrometres | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
| '''Multiple budding "steering wheel" appearance''' | | '''Multiple budding "steering wheel" appearance''' | ||
| Clinical??? | | Clinical??? | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref> | ||
| [ | | [[Image:Paracoccidioides_brasiliensis_01.jpg |thumb|center|150px|P. brasiliensis (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
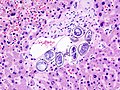
| Pneumocystis jirovecii ( | | Pneumocystis jirovecii ([[pneumocystis carinii pneumonia]]; abbrev. PCP) | ||
| Fungi (previously thought to be a protozoan) | | Fungi (previously thought to be a protozoan) | ||
| 7-8 micrometres | | 7-8 micrometres | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
| GMS | | GMS | ||
| Usually in clusters of '''alveolar casts with a honeycomb appearance''' | | Usually in clusters of '''alveolar casts with a honeycomb appearance''' | ||
| HIV/AIDS associated | | [[HIV]]/AIDS associated | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR684>{{Ref APBR|684}}</ref> | ||
| [ | | [[Image:Pneumocystosis_carinii_of_lung_in_AIDS_959_lores.jpg|thumb|center|150px| PCP. (WC)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Cryptococcus ([[cryptococcosis]]) | ||
| Fungi | | Fungi | ||
| 5-15 micrometres | | 5-15 micrometres | ||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
| '''Prominent (i.e. thick polysaccharide) capsule''' | | '''Prominent (i.e. thick polysaccharide) capsule''' | ||
| HIV/AIDS associated, most common CNS fungus | | HIV/AIDS associated, most common CNS fungus | ||
| <ref>APBR | | <ref name=Ref_APBR682>{{Ref APBR|682}}</ref> | ||
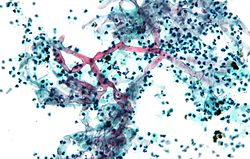
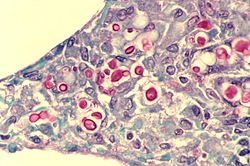
| [ | | [[Image:Cryptococcosis_of_lung_in_patient_with_AIDS._Mucicarmine_stain_962_lores.jpg |thumb|center|150px| Crytococcosis - mucicarmine (WC)]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Notes: | Notes: | ||
*'''Bold''' text = key features. | *'''Bold''' text = key features. | ||
==Fungi | =Fungi= | ||
{{Main|Fungi}} | |||
*There are lots of 'em. Below are a few of 'em. | *There are lots of 'em. Below are a few of 'em. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 111: | ||
===Tissue invasive fungi=== | ===Tissue invasive fungi=== | ||
Typically:<ref>CM 17 Apr 2009.</ref> | Typically:<ref>CM 17 Apr 2009.</ref> | ||
*Mucor | *Mucor. | ||
*Aspergillus | *Aspergillus. | ||
== | ===List=== | ||
* | *[[Histoplasmosis]]. | ||
** | *[[Coccidioidomycosis]]. | ||
** | *[[Pneumocystis pneumonia]]. | ||
*[[Cryptococcus]]. | |||
*[[Cryptosporidiosis]]. | |||
*[[Candidiasis]]. | |||
*[[Blastomycosis]]. | |||
*[[Mucormycosis]]. | |||
== | =Worms & stuff= | ||
== | ==Schistosomiasis== | ||
:''See [[Urine cytopathology]]''. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Trematode, i.e. type of worm. | |||
* | |||
*Due to: | |||
* | **''Schistosoma mansoni''. | ||
* | **''Schistosoma haematobium''. | ||
**''Schistosoma japonicum'' | |||
*''S. haematobium'' infection associated with [[squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder]]. | |||
**Classically presents with hematuria. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features of ova (''S. haematobium''):<ref>URL: [http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case622/dx.html http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case622/dx.html]. Accessed on: 26 January 2012.</ref> | |||
* Elliptical ~140 micrometres max dimension. | |||
* "Spike" approx. the size of a [[PMN]]. | |||
**" | |||
Images: | ====Images==== | ||
*[http:// | <gallery> | ||
*[http:// | Image:Schistosomiasis_haematobia.jpg | Schistosomiasis haematobia. (WC) | ||
Image:Schistosoma japonicum (1) histopathology.JPG | Schistosoma japonicum. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Schistosoma japonicum (2) histopathology.JPG | Schistosoma japonicum. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Schistosoma japonicum (3) histopathology.JPG | Schistosoma japonicum. (WC/KGH) | |||
Image:Schistosoma_-_intermed_mag.jpg | Schistosoma eggs - intermed. mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
Image:Schistosoma_-_very_high_mag.jpg | Schistosoma eggs - very high mag. (WC/Nephron) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case622.html Schistosomiasis - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case622/images/fig08.jpg Comparison of Schistosome eggs (upmc.edu/Lancet)]. | |||
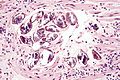
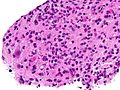
==Toxoplasma== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Common CNS infection. | |||
**''Toxoplasma gondii'' - pathogenic; causes ''toxoplasmosis''. | |||
*Previously classified as a ''protozoa''. | |||
*A [[TORCH infection]]. | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
General: | |||
*Tachyzoites (Invasive form): | |||
**Crescent-shaped organisms that are 2-3μm wide by 4-8μm long. | |||
*Bradyzoites: | |||
**Are founded within the tissue cysts and are shorter than tachyzoites. | |||
*Oocysst: | |||
**Ovoid shape that measures 10μm to 12μm and contains four sporozoites. | |||
*Histopathological features depend on location in body. | |||
* | |||
====Lymph node==== | |||
LN features:<ref name=Ref_ILNP113>{{Ref ILNP|113}}</ref> | |||
*Reactive germinal centers (pale areas - larger than usual). | |||
**Often poorly demarcated - due to loose epithelioid cell clusters at germinal center edge - '''key feature'''. | |||
*Epithelioid cells - perifollicular & intrafollicular. | |||
**Loose aggregates of histiocytes (do not form round granulomas): | |||
***Abundant pale cytoplasm. | |||
***Nucleoli. | |||
*Monocytoid cells (monocyte-like cells) - in cortex & paracortex. | |||
**Large cells in islands/sheets '''key feature''' with: | |||
***Abundant pale cytoplasm - '''important'''. | |||
***Well-defined cell border - '''important'''. | |||
***Singular nucleus. | |||
**Cell clusters usually have interspersed neutrophils. | |||
Images (lymph node): | |||
*[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Toxoplasmosis_lymphadenopathy_-_low_mag.jpg Toxoplasmosis - low mag. (WC)]. | |||
* | *[http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Toxoplasmosis_lymphadenopathy_-_high_mag.jpg Toxoplasmosis - high mag. (WC)]. | ||
== | ====CNS==== | ||
CNS features:<ref>URL: [http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm]. Accessed on: 19 October 2010.</ref> | |||
*Granular appearing ball ~ 2x the size of resting lymphocyte. | |||
=====Images (CNS)===== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Toxoplasmosis_-_cropped_-_very_high_mag.jpg | CNS toxoplasmosis - very high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Toxoplasmosis_-_ihc_-_very_high_mag.jpg | CNS toxoplasmosis - IHC - very high mag. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm CNS toxoplasmosis (ouhsc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/Composites/FND5IE01-Toxoplasmosis-Micro.htm CNS toxoplasmosis (ouhsc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case350.html Toxoplasmosis - several images (upmc.edu)]. | |||
== | ====Heart==== | ||
=== | Features: | ||
*Intramuscular organisms. | |||
* | |||
DDx: | |||
*[[Chagas disease]]. (???) | |||
* | |||
Images (heart): | |||
*[http:// | *[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case160.html Toxoplasmosis (upmc.edu)]. | ||
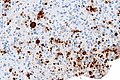
== | ===IHC=== | ||
*IHC for toxoplasma.<ref>URL: [http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm]. Accessed on: 19 October 2010.</ref> | |||
==Strongyloides== | ==Strongyloidiasis== | ||
* | ===General=== | ||
*Causes by worm ''Strongyloides stercoralis''. | |||
*High case mortality rate ~ 70%.<ref name=pmid15337730>{{Cite journal | last1 = Lim | first1 = S. | last2 = Katz | first2 = K. | last3 = Krajden | first3 = S. | last4 = Fuksa | first4 = M. | last5 = Keystone | first5 = JS. | last6 = Kain | first6 = KC. | title = Complicated and fatal Strongyloides infection in Canadians: risk factors, diagnosis and management. | journal = CMAJ | volume = 171 | issue = 5 | pages = 479-84 | month = Aug | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1503/cmaj.1031698 | PMID = 15337730 }}</ref> | |||
*May present after years of latency due to immune suppression.<ref name=pmid11528578>{{Cite journal | last1 = Siddiqui | first1 = AA. | last2 = Berk | first2 = SL. | title = Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. | journal = Clin Infect Dis | volume = 33 | issue = 7 | pages = 1040-7 | month = Oct | year = 2001 | doi = 10.1086/322707 | PMID = 11528578 }}</ref> | |||
Location: | |||
*Lung. (???) | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Long worms. | *Long worms. | ||
*~10-15 micrometers wide. | *~10-15 micrometers wide. | ||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Strongyloides_stercoralis_larva.jpg | Strongyloides. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.totallyfreeimages.com/121316/This-micrograph-reveals-adult-strongyloides-nematodes-located-am Strongyloides (CDC/totallyfreeimages.com)]. | |||
*[http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/116331/enlarge Strongyloides (sciencephoto.com)]. | |||
==Echinococcus== | ==Echinococcus== | ||
*Echinococcus granulosus. | *Several species - most common: ''Echinococcus granulosus''. | ||
*Causes ''hydatid disease'' in the liver. | *Causes ''[[hydatid disease]]'' in the [[liver]]. | ||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | Features: | ||
*Hooklets. | *Laminated wall +/- calcification.<ref name=Ref_PBPoD8_448>{{Ref PCPBoD8|448}}</ref> | ||
*Scoleces - knoblike anterior end of a tapeworm.<ref>[http://www.thefreedictionary.com/scoleces http://www.thefreedictionary.com/scoleces]. Accessed on: 10 January 2010.</ref> | *Organisms: | ||
**Hooklets. | |||
**Scoleces - knoblike anterior end of a tapeworm.<ref>[http://www.thefreedictionary.com/scoleces http://www.thefreedictionary.com/scoleces]. Accessed on: 10 January 2010.</ref> | |||
==Enterobius vermicularis== | ==Enterobius vermicularis== | ||
*AKA ''pinworm''. | *AKA ''pinworm''. | ||
===General=== | |||
*Classically found in a [[vermiform appendix]] removed for appendicitis that does not have [[acute appendicitis]].<ref name=pmid7945067>{{Cite journal | last1 = Dahlstrom | first1 = JE. | last2 = Macarthur | first2 = EB. | title = Enterobius vermicularis: a possible cause of symptoms resembling appendicitis. | journal = Aust N Z J Surg | volume = 64 | issue = 10 | pages = 692-4 | month = Oct | year = 1994 | doi = | PMID = 7945067 }}</ref> | |||
**See: ''[[Vermiform appendix#Enterobius vermicularis]]''. | |||
===Gross=== | |||
* | *Peri-anal white squiggly thing ~ 2-13 mm in length. | ||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.dijitalimaj.com/alamyDetail.aspx?img={14157DA6-DBE8-4E03-BE4A-69591588E153} Pinworm (dijitalimaj.com)]. | |||
== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features - organism: | |||
*0.2-0.5 mm width x 2-13 mm length. | |||
*Characteristic triangular "spikes" seen on cross section - base x height ~ 30 x 30 μm. | |||
**''Spikes'' is in quotations, as these are really a longitudinal blade-like ridges, that run the length of the worm. | |||
Features - eggs:<ref name=Ref_APBR685>{{Ref APBR|685}}</ref> | |||
*Ovoid - double walled shells, one side flat. | |||
* | |||
Images: | ====Images==== | ||
*[http://www. | www: | ||
* | *[http://www.brown.edu/Courses/Digital_Path/systemic_path/GI/enterobius.html Enterobius (brown.edu)]. | ||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Enterobius_-_very_low_mag.jpg | Enterobius - very low mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Enterobius_-_high_mag.jpg | Enterobius - high mag. (WC) | |||
Image:Pinworms_in_the_Appendix_%281%29.jpg | Pinworm (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Trichinella== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Causes ''Trichinosis''. | |||
**Classically associated with uncooked pork.<ref name=pmid17072975>{{cite journal |author=Kaewpitoon N, Kaewpitoon SJ, Philasri C, ''et al.'' |title=Trichinosis: epidemiology in Thailand |journal=World J. Gastroenterol. |volume=12 |issue=40 |pages=6440–5 |year=2006 |month=October |pmid=17072975 |doi= |url=http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/12/6440.asp}}</ref> | |||
*Several types; most due to ''T. spiralis''.<ref name=pmid17072975/> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | |||
*Worm. | |||
Image: | |||
* | *[http://www.microbiologybytes.com/introduction/Paraquiz/QUIZ06A.html Muscle bx with trichinella (microbiologybytes.com)]. | ||
*[http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/jpeg2/MUSC010.jpg Trichinella (med.utah.edu)].<ref>URL: [http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/EXAM/IMGQUIZ/msfrm.html http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/EXAM/IMGQUIZ/msfrm.html]. Accessed on: 5 December 2010.</ref> | |||
=== | ==Cysticercosis== | ||
===General=== | |||
*Caused by ''Taenia solium''; pork tapeworm. | |||
*May cause [[epilepsy]]; most common parasitic CNS infection.<ref name=pmid19208982>{{cite journal |author=Prasad KN, Prasad A, Verma A, Singh AK |title=Human cysticercosis and Indian scenario: a review |journal=J. Biosci. |volume=33 |issue=4 |pages=571–82 |year=2008 |month=November |pmid=19208982 |doi= |url=}}</ref> | |||
* | |||
===Gross=== | |||
*Multiple cystic spaces. | |||
Image: | Image: | ||
*[http:// | *[http://reference.medscape.com/features/slideshow/neurocysticercosis Neurocysticercosis (medscape.com)]. | ||
== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Large ovoid body with complex structures (cross-section of worm) - size: millimetres. | ||
* | **+/-External eosinophilic microvilli. | ||
**+/-Gastrointestinal tract - ovoid structure within the worm. | |||
Notes: | |||
*Histomorphology is not distinctive for the type... microbiology usually figures it out. | |||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http:// | *[http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/html/imagelibrary/A-F/Cysticercosis/body_Cysticercosis_il1.htm Cysticercosis (cdc.gov)]. | ||
*[http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/116340/enlarge Cysticercosis (sciencephoto.com)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case154.html Neurocysticercosis - case 1 (upmc.edu)]. | |||
*[http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case376.html Neurocysticercosis - case 2 (upmc.edu)]. | |||
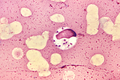
==Rhinosporidiosis== | |||
:'''''Not''' to be confused with [[rhinoscleroma]]''. | |||
===General=== | |||
*Caused by parasite ''Rinosporidium seeberi''. | |||
**India, Sri Lanka. | |||
*Nasal mass. | |||
**May present with obstruction.<ref name=pmid16945122/> | |||
== | ===Microscopic=== | ||
Features: | Features:<ref>URL: [http://www.histopathology-india.net/Rhino.htm http://www.histopathology-india.net/Rhino.htm]. Accessed on: 4 January 2012.</ref><ref name=pmid16945122/> | ||
*Globular cysts ~ 100 micrometers with endospores: | |||
** | **Hyperchromatic (blue) spherical 10-100 micrometer. | ||
Images: | Images: | ||
*[http:// | *[http://www.arquivosdeorl.org.br/conteudo/imagesFORL/11-02-19-fig01-ing.gif Rhinosporidiosis (arquivosdeorl.org.br)].<ref>URL: [http://www.arquivosdeorl.org.br/conteudo/acervo_eng.asp?id=428 http://www.arquivosdeorl.org.br/conteudo/acervo_eng.asp?id=428]. 4 January 2012.</ref> | ||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1560165/figure/F1/ Rhinosporidiosis (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid16945122>{{Cite journal | last1 = Morelli | first1 = L. | last2 = Polce | first2 = M. | last3 = Piscioli | first3 = F. | last4 = Del Nonno | first4 = F. | last5 = Covello | first5 = R. | last6 = Brenna | first6 = A. | last7 = Cione | first7 = A. | last8 = Licci | first8 = S. | title = Human nasal rhinosporidiosis: an Italian case report. | journal = Diagn Pathol | volume = 1 | issue = | pages = 25 | month = | year = 2006 | doi = 10.1186/1746-1596-1-25 | PMID = 16945122 |PMC = 1560165 | URL = http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1560165/?tool=pubmed}}</ref> | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1560165/figure/F2/ Rhinosporidiosis (nih.gov)]. | |||
===Stains=== | |||
*[[GMS stain]] +ve organisms. | |||
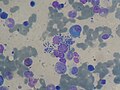
==Leishmaniasis== | |||
===General=== | |||
*Caused by protozoa in the group ''Leishmania'' group. | |||
*Transmitted to humans by the ''sand fly''. | |||
== | May be: | ||
*Cutaneous.<ref name=pmid20377337>{{Cite journal | last1 = Goto | first1 = H. | last2 = Lindoso | first2 = JA. | title = Current diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. | journal = Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther | volume = 8 | issue = 4 | pages = 419-33 | month = Apr | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1586/eri.10.19 | PMID = 20377337 }}</ref> | |||
*Mucocutaneous.<ref name=pmid20377337/> | |||
*Visceral.<ref name=pmid19708817>{{Cite journal | last1 = den Boer | first1 = ML. | last2 = Alvar | first2 = J. | last3 = Davidson | first3 = RN. | last4 = Ritmeijer | first4 = K. | last5 = Balasegaram | first5 = M. | title = Developments in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis. | journal = Expert Opin Emerg Drugs | volume = 14 | issue = 3 | pages = 395-410 | month = Sep | year = 2009 | doi = 10.1517/14728210903153862 | PMID = 19708817 }}</ref> | |||
===Microscopic=== | |||
Features: | Features: | ||
* | *Small ~1-2 micrometers. | ||
====Images==== | |||
<gallery> | |||
Image:Leishmania_donovani_01.png | Leishmania - smear. (WC) | |||
Image:Leishmania_2009-04-14_smear.JPG | Leishmania - bone marrow. (WC) | |||
Image:Cutaneous_Leishmaniasis_x100 | Leishmania - cutaneous. (WC) | |||
</gallery> | |||
www: | |||
*[http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/leishmaniasis/index.html Leishmania and sand fly (cdc.gov)]. | |||
===Stains=== | |||
*[[Giemsa stain]] - highlights organisms. | |||
=Viruses= | |||
{{Main|Viruses}} | |||
This is a fairly big topic. There are about half a dozen viral inclusions (e.g. [[CMV]], [[HSV]], [[VZV]], [[adenovirus]]) a decent pathologist ought to be able to identify. The ''virus'' article covers 'em. | |||
=Bacteria= | |||
{{Main|Bacteria}} | |||
This is a small topic when considered from the perspective of an anatomical pathologist. Most stuff is sorted-out by microbiology. | |||
=Protozoa= | |||
A historical category of organisms. Lifeforms previously categorized as ''protozoa'' are in several different ''kingdoms''. | |||
{{Main|Amebiasis}} | |||
{{Main|Leishmaniasis}} | |||
{{Main|Pneumocystis jirovecii}} | |||
{{Main|Toxoplasma}} | |||
=Microorganisms and cancer= | |||
==Viruses and cancer== | |||
A number of microorganisms are associated with the development of cancer:<ref>{{Ref PCPBoD8|168}}</ref> | |||
*[[Human papillomavirus]] (HPV) - cancer of cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, head & neck. | |||
*[[Epstein-Barr virus]] - [[Burkitt lymphoma]], [[Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder]], classical [[Hodgkin lymphoma]] (all but ''[[Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma|nodular sclerosis HL]]''), [[nasopharyngeal carcinoma]]. | |||
*[[Hepatitis B]] - [[HCC]]. | |||
*[[Hepatitis C]] - [[HCC]]. | |||
*[[Lymphoma#Adult_T-cell_leukemia.2Flymphoma|Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I]] (HTLV-1) - [[Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma]]. | |||
*[[Human herpesvirus-8]] (HHV-8) - [[Kaposi sarcoma]], [[primary effusion lymphoma]], body cavity lymphoma. | |||
*[[Merkel cell carcinoma|Merkel cell polyomavirus]] - [[Merkel cell carcinoma]]. | |||
==Bacteria and cancer== | |||
*[[Helicobacter pylori]] - [[MALT lymphoma]], [[gastric carcinoma]]. | |||
==Parasites and cancer== | |||
*[[Schistosoma haematobium]] - [[squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder]]. | |||
*Clonorchis sinensis (AKA Opisthorchis sinensis) - [[cholangiocarcinoma]]. | |||
*Opisthorchis viverrini - [[cholangiocarcinoma]]. | |||
=See also= | |||
*[[Staining]]. | *[[Staining]]. | ||
*[[Immunohistochemistry]]. | *[[Immunohistochemistry]]. | ||
*[[Viruses]]. | |||
=References= | |||
{{reflist|2}} | {{reflist|2}} | ||
=External links= | |||
*[http://www.fujita-hu.ac.jp/~tsutsumi/index.html Pathology of Infectious Diseases (fujita-hu.ac.jp)]. | |||
[[Category:Basics]] | [[Category:Basics]] | ||
[[Category:Microorganisms]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:43, 4 December 2023
Microorganisms show-up every once in a while. It is essential to know 'em.
Microorganisms
Fungi
| Name (disease) | Kingdom | Size | Shape | Stains | Other (microscopic) | Clinical | References | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspergillus (aspergillosis) | Fungi | ? | Hyphae that branching with 45 degrees angle |
PAS-D | Fruiting heads when aerobic | ? Immunosuppression | [1] | |
| Zygomycota (zygomycosis); more specific Mucorales (mucormycosis) |
Fungi | ? | Branching hyphae with variable width | ? | Granulomata assoc. | Diabetes, immunodeficient | [1] | |
| Coccidioides, usually C. immitis (coccidioidomycosis) |
Fungi | Large - 20-60 micrometers, endospores 1-5 micrometers |
Spherules | Stains? | Other? | Immunodeficient | [1] | Coccidioidomycosis (med.sc.edu) |
| Histoplasma (histoplasmosis) | Fungi | 2-5 micrometers | Spherical | GMS | Intracellular (unlike candida), granulomata | Source: soil with bird droppings | [1] | |
| Blastomyces (blastomycosis) | Fungi | 5-15 micrometres | Spherical (yeast) | Stains? | Granulomas, broad-based budding yeast | Habitat: Northeast America, Africa | [1][2] | |
| Paracoccidioides (paracoccidioidomycosis) | Fungi | 6-60 micrometres | Spherical (yeast) | Stains? | Multiple budding "steering wheel" appearance | Clinical??? | [1] | |
| Pneumocystis jirovecii (pneumocystis carinii pneumonia; abbrev. PCP) | Fungi (previously thought to be a protozoan) | 7-8 micrometres | "Dented ping-pong ball" | GMS | Usually in clusters of alveolar casts with a honeycomb appearance | HIV/AIDS associated | [3] | |
| Cryptococcus (cryptococcosis) | Fungi | 5-15 micrometres | Yeast | GMS | Prominent (i.e. thick polysaccharide) capsule | HIV/AIDS associated, most common CNS fungus | [1] |
Notes:
- Bold text = key features.
Fungi
- There are lots of 'em. Below are a few of 'em.
Terminology:[4]
- Hyphae = microscopic filamentous growth (of fungi) -- single cell.
- Mycelial = filamentous network of hyphae.
- Septae/septation = hyphae may be subdivided by septae -- if they aren't they are one mass of protoplasm. (?)
- Dimorphism = exist in two forms; e.g. single cell (yeast) and mycelial growth.
- Pseudohyphae = looks like hyphae --but branching pattern is created by separate cells.[5]
Tissue invasive fungi
Typically:[6]
- Mucor.
- Aspergillus.
List
- Histoplasmosis.
- Coccidioidomycosis.
- Pneumocystis pneumonia.
- Cryptococcus.
- Cryptosporidiosis.
- Candidiasis.
- Blastomycosis.
- Mucormycosis.
Worms & stuff
Schistosomiasis
- See Urine cytopathology.
General
- Trematode, i.e. type of worm.
- Due to:
- Schistosoma mansoni.
- Schistosoma haematobium.
- Schistosoma japonicum
- S. haematobium infection associated with squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder.
- Classically presents with hematuria.
Microscopic
Features of ova (S. haematobium):[7]
- Elliptical ~140 micrometres max dimension.
- "Spike" approx. the size of a PMN.
Images
www:
Toxoplasma
General
- Common CNS infection.
- Toxoplasma gondii - pathogenic; causes toxoplasmosis.
- Previously classified as a protozoa.
- A TORCH infection.
Microscopic
General:
- Tachyzoites (Invasive form):
- Crescent-shaped organisms that are 2-3μm wide by 4-8μm long.
- Bradyzoites:
- Are founded within the tissue cysts and are shorter than tachyzoites.
- Oocysst:
- Ovoid shape that measures 10μm to 12μm and contains four sporozoites.
- Histopathological features depend on location in body.
Lymph node
LN features:[8]
- Reactive germinal centers (pale areas - larger than usual).
- Often poorly demarcated - due to loose epithelioid cell clusters at germinal center edge - key feature.
- Epithelioid cells - perifollicular & intrafollicular.
- Loose aggregates of histiocytes (do not form round granulomas):
- Abundant pale cytoplasm.
- Nucleoli.
- Loose aggregates of histiocytes (do not form round granulomas):
- Monocytoid cells (monocyte-like cells) - in cortex & paracortex.
- Large cells in islands/sheets key feature with:
- Abundant pale cytoplasm - important.
- Well-defined cell border - important.
- Singular nucleus.
- Cell clusters usually have interspersed neutrophils.
- Large cells in islands/sheets key feature with:
Images (lymph node):
CNS
CNS features:[9]
- Granular appearing ball ~ 2x the size of resting lymphocyte.
Images (CNS)
www:
- CNS toxoplasmosis (ouhsc.edu).
- CNS toxoplasmosis (ouhsc.edu).
- Toxoplasmosis - several images (upmc.edu).
Heart
Features:
- Intramuscular organisms.
DDx:
- Chagas disease. (???)
Images (heart):
IHC
- IHC for toxoplasma.[10]
Strongyloidiasis
General
- Causes by worm Strongyloides stercoralis.
- High case mortality rate ~ 70%.[11]
- May present after years of latency due to immune suppression.[12]
Location:
- Lung. (???)
Microscopic
Features:
- Long worms.
- ~10-15 micrometers wide.
Images
www:
Echinococcus
- Several species - most common: Echinococcus granulosus.
- Causes hydatid disease in the liver.
Microscopic
Features:
- Laminated wall +/- calcification.[13]
- Organisms:
- Hooklets.
- Scoleces - knoblike anterior end of a tapeworm.[14]
Enterobius vermicularis
- AKA pinworm.
General
- Classically found in a vermiform appendix removed for appendicitis that does not have acute appendicitis.[15]
Gross
- Peri-anal white squiggly thing ~ 2-13 mm in length.
Image:
Microscopic
Features - organism:
- 0.2-0.5 mm width x 2-13 mm length.
- Characteristic triangular "spikes" seen on cross section - base x height ~ 30 x 30 μm.
- Spikes is in quotations, as these are really a longitudinal blade-like ridges, that run the length of the worm.
Features - eggs:[16]
- Ovoid - double walled shells, one side flat.
Images
www:
Trichinella
General
- Causes Trichinosis.
- Classically associated with uncooked pork.[17]
- Several types; most due to T. spiralis.[17]
Microscopic
Features:
- Worm.
Image:
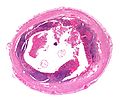
Cysticercosis
General
- Caused by Taenia solium; pork tapeworm.
- May cause epilepsy; most common parasitic CNS infection.[19]
Gross
- Multiple cystic spaces.
Image:
Microscopic
Features:
- Large ovoid body with complex structures (cross-section of worm) - size: millimetres.
- +/-External eosinophilic microvilli.
- +/-Gastrointestinal tract - ovoid structure within the worm.
Notes:
- Histomorphology is not distinctive for the type... microbiology usually figures it out.
Images:
- Cysticercosis (cdc.gov).
- Cysticercosis (sciencephoto.com).
- Neurocysticercosis - case 1 (upmc.edu).
- Neurocysticercosis - case 2 (upmc.edu).
Rhinosporidiosis
- Not to be confused with rhinoscleroma.
General
- Caused by parasite Rinosporidium seeberi.
- India, Sri Lanka.
- Nasal mass.
- May present with obstruction.[20]
Microscopic
- Globular cysts ~ 100 micrometers with endospores:
- Hyperchromatic (blue) spherical 10-100 micrometer.
Images:
- Rhinosporidiosis (arquivosdeorl.org.br).[22]
- Rhinosporidiosis (nih.gov).[20]
- Rhinosporidiosis (nih.gov).
Stains
- GMS stain +ve organisms.
Leishmaniasis
General
- Caused by protozoa in the group Leishmania group.
- Transmitted to humans by the sand fly.
May be:
Microscopic
Features:
- Small ~1-2 micrometers.
Images
- Cutaneous Leishmaniasis x100
Leishmania - cutaneous. (WC)
www:
Stains
- Giemsa stain - highlights organisms.
Viruses
This is a fairly big topic. There are about half a dozen viral inclusions (e.g. CMV, HSV, VZV, adenovirus) a decent pathologist ought to be able to identify. The virus article covers 'em.
Bacteria
This is a small topic when considered from the perspective of an anatomical pathologist. Most stuff is sorted-out by microbiology.
Protozoa
A historical category of organisms. Lifeforms previously categorized as protozoa are in several different kingdoms.
Microorganisms and cancer
Viruses and cancer
A number of microorganisms are associated with the development of cancer:[25]
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) - cancer of cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, head & neck.
- Epstein-Barr virus - Burkitt lymphoma, Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, classical Hodgkin lymphoma (all but nodular sclerosis HL), nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
- Hepatitis B - HCC.
- Hepatitis C - HCC.
- Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-1) - Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
- Human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) - Kaposi sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, body cavity lymphoma.
- Merkel cell polyomavirus - Merkel cell carcinoma.
Bacteria and cancer
Parasites and cancer
- Schistosoma haematobium - squamous cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder.
- Clonorchis sinensis (AKA Opisthorchis sinensis) - cholangiocarcinoma.
- Opisthorchis viverrini - cholangiocarcinoma.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 682. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mycology/mycology-6.htm
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 684. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ http://www.fungionline.org.uk/1intro/3growth_forms.html
- ↑ http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mycology/mycology-3.htm
- ↑ CM 17 Apr 2009.
- ↑ URL: http://path.upmc.edu/cases/case622/dx.html. Accessed on: 26 January 2012.
- ↑ Ioachim, Harry L; Medeiros, L. Jeffrey (2008). Ioachim's Lymph Node Pathology (4th ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 113. ISBN 978-0781775960.
- ↑ URL: http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm. Accessed on: 19 October 2010.
- ↑ URL: http://moon.ouhsc.edu/kfung/jty1/opaq/PathQuiz/N0I001-PQ01-M.htm. Accessed on: 19 October 2010.
- ↑ Lim, S.; Katz, K.; Krajden, S.; Fuksa, M.; Keystone, JS.; Kain, KC. (Aug 2004). "Complicated and fatal Strongyloides infection in Canadians: risk factors, diagnosis and management.". CMAJ 171 (5): 479-84. doi:10.1503/cmaj.1031698. PMID 15337730.
- ↑ Siddiqui, AA.; Berk, SL. (Oct 2001). "Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection.". Clin Infect Dis 33 (7): 1040-7. doi:10.1086/322707. PMID 11528578.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 448. ISBN 978-1416054542.
- ↑ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/scoleces. Accessed on: 10 January 2010.
- ↑ Dahlstrom, JE.; Macarthur, EB. (Oct 1994). "Enterobius vermicularis: a possible cause of symptoms resembling appendicitis.". Aust N Z J Surg 64 (10): 692-4. PMID 7945067.
- ↑ Lefkowitch, Jay H. (2006). Anatomic Pathology Board Review (1st ed.). Saunders. pp. 685. ISBN 978-1416025887.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Kaewpitoon N, Kaewpitoon SJ, Philasri C, et al. (October 2006). "Trichinosis: epidemiology in Thailand". World J. Gastroenterol. 12 (40): 6440–5. PMID 17072975. http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/12/6440.asp.
- ↑ URL: http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/EXAM/IMGQUIZ/msfrm.html. Accessed on: 5 December 2010.
- ↑ Prasad KN, Prasad A, Verma A, Singh AK (November 2008). "Human cysticercosis and Indian scenario: a review". J. Biosci. 33 (4): 571–82. PMID 19208982.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 Morelli, L.; Polce, M.; Piscioli, F.; Del Nonno, F.; Covello, R.; Brenna, A.; Cione, A.; Licci, S. (2006). "Human nasal rhinosporidiosis: an Italian case report.". Diagn Pathol 1: 25. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-1-25. PMC 1560165. PMID 16945122. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1560165/.
- ↑ URL: http://www.histopathology-india.net/Rhino.htm. Accessed on: 4 January 2012.
- ↑ URL: http://www.arquivosdeorl.org.br/conteudo/acervo_eng.asp?id=428. 4 January 2012.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Goto, H.; Lindoso, JA. (Apr 2010). "Current diagnosis and treatment of cutaneous and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis.". Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 8 (4): 419-33. doi:10.1586/eri.10.19. PMID 20377337.
- ↑ den Boer, ML.; Alvar, J.; Davidson, RN.; Ritmeijer, K.; Balasegaram, M. (Sep 2009). "Developments in the treatment of visceral leishmaniasis.". Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 14 (3): 395-410. doi:10.1517/14728210903153862. PMID 19708817.
- ↑ Mitchell, Richard; Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul K.; Aster, Jon (2011). Pocket Companion to Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (8th ed.). Elsevier Saunders. pp. 168. ISBN 978-1416054542.