Difference between revisions of "Brain metastasis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Jensflorian (talk | contribs) (→General: Treatment) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ Infobox diagnosis | {{ Infobox diagnosis | ||
| Name = {{PAGENAME}} | | Name = {{PAGENAME}} | ||
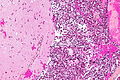
| Image = Metastatic_adenocarcinoma_-_cerebellum_-_high_mag.jpg | | Image = Metastatic_adenocarcinoma_-_cerebellum_-_high_mag.jpg | ||
| Width = | | Width = | ||
| Caption = Metastatic adenocarcinoma, compatible with colorectal primary. [[ | | Caption = Metastatic adenocarcinoma, compatible with colorectal primary. [[HPS stain]]. | ||
| Synonyms = | | Synonyms = | ||
| Micro = usu. well-demarcated border between brain and lesion, no cytoplasmic processes (seen in glial tumours), usu. have [[nuclear atypia]] of malignancy, +/-glandular architecture, +/-nucleoli seen | | Micro = usu. well-demarcated border between brain and lesion, no cytoplasmic processes (seen in glial tumours), usu. have [[nuclear atypia]] of malignancy, +/-glandular architecture, +/-nucleoli seen | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| Tx = surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy | | Tx = surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Brain metastasis''', also '''metastatic brain tumour''', is a [[brain tumour]] that arose elsewhere and spread to the brain. | '''Brain metastasis''', also '''metastatic brain tumour''',<ref>URL: [http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000769.htm http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000769.htm]. Accessed on: November 8, 2014.</ref> is a [[brain tumour]] that arose elsewhere and spread to the brain. | ||
==General== | ==General== | ||
*Most common brain tumour in adults.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pekmezci | first1 = M. | last2 = Perry | first2 = A. | title = Neuropathology of brain metastases. | journal = Surg Neurol Int | volume = 4 | issue = Suppl 4 | pages = S245-55 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.4103/2152-7806.111302 | PMID = 23717796 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Suki | first1 = D. | last2 = Khoury Abdulla | first2 = R. | last3 = Ding | first3 = M. | last4 = Khatua | first4 = S. | last5 = Sawaya | first5 = R. | title = Brain metastases in patients diagnosed with a solid primary cancer during childhood: experience from a single referral cancer center. | journal = J Neurosurg Pediatr | volume = 14 | issue = 4 | pages = 372-85 | month = Oct | year = 2014 | doi = 10.3171/2014.7.PEDS13318 | PMID = 25127097 }}</ref> | *Most common brain tumour in adults.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Pekmezci | first1 = M. | last2 = Perry | first2 = A. | title = Neuropathology of brain metastases. | journal = Surg Neurol Int | volume = 4 | issue = Suppl 4 | pages = S245-55 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.4103/2152-7806.111302 | PMID = 23717796 }}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Suki | first1 = D. | last2 = Khoury Abdulla | first2 = R. | last3 = Ding | first3 = M. | last4 = Khatua | first4 = S. | last5 = Sawaya | first5 = R. | title = Brain metastases in patients diagnosed with a solid primary cancer during childhood: experience from a single referral cancer center. | journal = J Neurosurg Pediatr | volume = 14 | issue = 4 | pages = 372-85 | month = Oct | year = 2014 | doi = 10.3171/2014.7.PEDS13318 | PMID = 25127097 }}</ref> | ||
*Common | ** Brain metastases are found in up to 25% cancer patients at autopsy. <ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Gavrilovic | first1 = IT. | last2 = Posner | first2 = JB. | title = Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. | journal = J Neurooncol | volume = 75 | issue = 1 | pages = 5-14 | month = Oct | year = 2005 | doi = 10.1007/s11060-004-8093-6 | PMID = 16215811 }}</ref> | ||
**Incidence of brain metastases increases with age. | |||
** 80% of brain metastases are located supratentorial, usu. at the border between white and grey matter. | |||
*In more than 50% there are multiple metastases in the brain. | |||
*Common primary sites (in order of prevalence): [[lung cancer|lung]], [[invasive breast cancer|breast]], [[renal cell carcinoma|kidney]], [[Gastrointestinal pathology|gastrointestinal]], [[melanoma]].<ref>{{Ref TN2007|NS9}}</ref> | |||
*Percentage of previously diagnosed cancers with brain metastases - by primary site: lung cancer 19.9%, melanoma 6.9%, breast cancer 5.1%, renal cancer 6.5%, colorectal cancer 1.8%.<ref name=pmid15254054>{{Cite journal | last1 = Barnholtz-Sloan | first1 = JS. | last2 = Sloan | first2 = AE. | last3 = Davis | first3 = FG. | last4 = Vigneau | first4 = FD. | last5 = Lai | first5 = P. | last6 = Sawaya | first6 = RE. | title = Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. | journal = J Clin Oncol | volume = 22 | issue = 14 | pages = 2865-72 | month = Jul | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149 | PMID = 15254054 }}</ref> | *Percentage of previously diagnosed cancers with brain metastases - by primary site: lung cancer 19.9%, melanoma 6.9%, breast cancer 5.1%, renal cancer 6.5%, colorectal cancer 1.8%.<ref name=pmid15254054>{{Cite journal | last1 = Barnholtz-Sloan | first1 = JS. | last2 = Sloan | first2 = AE. | last3 = Davis | first3 = FG. | last4 = Vigneau | first4 = FD. | last5 = Lai | first5 = P. | last6 = Sawaya | first6 = RE. | title = Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System. | journal = J Clin Oncol | volume = 22 | issue = 14 | pages = 2865-72 | month = Jul | year = 2004 | doi = 10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149 | PMID = 15254054 }}</ref> | ||
**''Lung'' followed by ''kidney'' is the order in a smaller series.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schouten | first1 = LJ. | last2 = Rutten | first2 = J. | last3 = Huveneers | first3 = HA. | last4 = Twijnstra | first4 = A. | title = Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. | journal = Cancer | volume = 94 | issue = 10 | pages = 2698-705 | month = May | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12173339 }}</ref> | **''Lung'' followed by ''kidney'' is the order in a smaller series.<ref>{{Cite journal | last1 = Schouten | first1 = LJ. | last2 = Rutten | first2 = J. | last3 = Huveneers | first3 = HA. | last4 = Twijnstra | first4 = A. | title = Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma. | journal = Cancer | volume = 94 | issue = 10 | pages = 2698-705 | month = May | year = 2002 | doi = | PMID = 12173339 }}</ref> | ||
*Treatment: Surgery 1-3 metastases, Stereotactic RT in 1-4(rarely up to 10) metastases, >4-10 metastases: Whole Brain RT. | |||
==Gross/Radiology== | ==Gross/Radiology== | ||
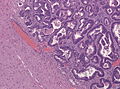
*Intra-axial location. | *Intra-axial location. | ||
**Typically at the grey-white junction.<ref name=pmid19727563>{{Cite journal | last1 = Della Puppa | first1 = A. | last2 = Dal Pos | first2 = S. | last3 = Zovato | first3 = S. | last4 = Orvieto | first4 = E. | last5 = Ciccarino | first5 = P. | last6 = Manara | first6 = R. | last7 = Zustovich | first7 = F. | last8 = Berti | first8 = F. | last9 = Gardiman | first9 = MP. | title = Solitary intra-ventricular brain metastasis from a breast carcinoma. | journal = J Neurooncol | volume = 97 | issue = 1 | pages = 123-6 | month = Mar | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s11060-009-9988-z | PMID = 19727563 }}</ref> | **Typically at the grey-white junction.<ref name=pmid19727563>{{Cite journal | last1 = Della Puppa | first1 = A. | last2 = Dal Pos | first2 = S. | last3 = Zovato | first3 = S. | last4 = Orvieto | first4 = E. | last5 = Ciccarino | first5 = P. | last6 = Manara | first6 = R. | last7 = Zustovich | first7 = F. | last8 = Berti | first8 = F. | last9 = Gardiman | first9 = MP. | title = Solitary intra-ventricular brain metastasis from a breast carcinoma. | journal = J Neurooncol | volume = 97 | issue = 1 | pages = 123-6 | month = Mar | year = 2010 | doi = 10.1007/s11060-009-9988-z | PMID = 19727563 }}</ref> | ||
Image: | |||
*[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3656562/figure/F1/ Brain metastases (nih.gov)].<ref name=pmid23717796 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Pekmezci | first1 = M. | last2 = Perry | first2 = A. | title = Neuropathology of brain metastases. | journal = Surg Neurol Int | volume = 4 | issue = Suppl 4 | pages = S245-55 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.4103/2152-7806.111302 | PMID = 23717796 }}</ref> | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:AFIP403613G-THYROID PAPILLARY CARCINOMA METASTATIC TO BRAIN.jpg | Well demarcated metastasis (WC/Dr. Kostich) | |||
File:BrainMetastasisFromBreastCancer.jpg | 3 brain metastases in breast cancer (WC/Jmarchn) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Microscopic== | ==Microscopic== | ||
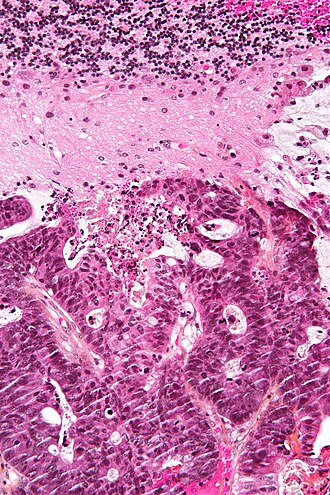
Appearance varies by subtype. | Appearance varies by subtype. | ||
Features of metastatic carcinoma: | Features of [[metastatic carcinoma]]: | ||
*Tubule formation/glands. | *Tubule formation/glands. | ||
*Usually well-circumscribed/sharply demarcated from surrounding tissue. | *Usually well-circumscribed/sharply demarcated from surrounding tissue. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 76: | ||
Image:Metastatic_adenocarcinoma_-_cerebellum_-_high_mag.jpg | CRC metastasis to cerebellum - high mag. (WC) | Image:Metastatic_adenocarcinoma_-_cerebellum_-_high_mag.jpg | CRC metastasis to cerebellum - high mag. (WC) | ||
Image:Brain metastasis - high mag.jpg | Brain metastasis - high mag. (WC) | Image:Brain metastasis - high mag.jpg | Brain metastasis - high mag. (WC) | ||
File:Adenocarcinoma infiltrating the brain.jpg | Adenocarcinoma of the lung metastasis. (WC/jensflorian) | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 87: | ||
**[[Clear cell renal cell carcinoma]]: PAX8 +ve, CK7 -ve, CK20 -ve, vimentin +ve, CD10 +ve. | **[[Clear cell renal cell carcinoma]]: PAX8 +ve, CK7 -ve, CK20 -ve, vimentin +ve, CD10 +ve. | ||
*Melanoma: S-100 +ve, HMB-45 +ve, Melan A +ve. | *Melanoma: S-100 +ve, HMB-45 +ve, Melan A +ve. | ||
*GFAP -ve.<ref name=pmid23717796 >{{Cite journal | last1 = Pekmezci | first1 = M. | last2 = Perry | first2 = A. | title = Neuropathology of brain metastases. | journal = Surg Neurol Int | volume = 4 | issue = Suppl 4 | pages = S245-55 | month = | year = 2013 | doi = 10.4103/2152-7806.111302 | PMID = 23717796 }}</ref> | |||
Other glial markers (suggest primary):<ref name=pmid23717796/> | |||
*OLIG2, SOX2. | |||
<gallery> | |||
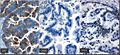
File:Immunhistochemie Bronchialkarzinom.jpg | CK7+/CK20-/TTF1+ profile in pulmonary adenocarcinoma metastasis. (WC/Marvin101) | |||
</gallery> | |||
==Origin== | |||
===Breast=== | |||
*8-30% BM. | |||
*Triple-negative cases have a poor prognosis. | |||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Neuropathology tumours]]. | *[[Neuropathology tumours]]. | ||
| Line 82: | Line 108: | ||
[[Category:Neuropathology]] | [[Category:Neuropathology]] | ||
[[Category:Diagnosis]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:04, 26 April 2024
| Brain metastasis | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
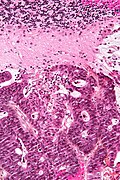
 Metastatic adenocarcinoma, compatible with colorectal primary. HPS stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | usu. well-demarcated border between brain and lesion, no cytoplasmic processes (seen in glial tumours), usu. have nuclear atypia of malignancy, +/-glandular architecture, +/-nucleoli seen |
| LM DDx | primary brain tumour - see primary brain tumour versus secondary brain tumour |
| IHC | GFAP -ve, dependent on primary - typical +ve for keratins (as carcinoma) |
| Site | brain |
|
| |
| Prevalence | most common brain tumour (adults) |
| Radiology | intra-axial, typically grey-white junction, cerebellum (esp. in adults) |
| Prognosis | poor |
| Clin. DDx | primary brain tumour, cerebral abscess or infection |
| Treatment | surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy |
Brain metastasis, also metastatic brain tumour,[1] is a brain tumour that arose elsewhere and spread to the brain.
General
- Most common brain tumour in adults.[2][3]
- Brain metastases are found in up to 25% cancer patients at autopsy. [4]
- Incidence of brain metastases increases with age.
- 80% of brain metastases are located supratentorial, usu. at the border between white and grey matter.
- In more than 50% there are multiple metastases in the brain.
- Common primary sites (in order of prevalence): lung, breast, kidney, gastrointestinal, melanoma.[5]
- Percentage of previously diagnosed cancers with brain metastases - by primary site: lung cancer 19.9%, melanoma 6.9%, breast cancer 5.1%, renal cancer 6.5%, colorectal cancer 1.8%.[6]
- Lung followed by kidney is the order in a smaller series.[7]
- Treatment: Surgery 1-3 metastases, Stereotactic RT in 1-4(rarely up to 10) metastases, >4-10 metastases: Whole Brain RT.
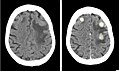
Gross/Radiology
- Intra-axial location.
- Typically at the grey-white junction.[8]
Image:
Microscopic
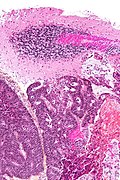
Appearance varies by subtype.
Features of metastatic carcinoma:
- Tubule formation/glands.
- Usually well-circumscribed/sharply demarcated from surrounding tissue.
- Usually nuclear atypia including:
- Nuclear hyperchromasia.
- Variation of nuclear size.
- Variation of nuclear shape.
- Mitoses - common.
DDx:
- Primary brain tumour - see primary brain tumour versus secondary brain tumour.
Images
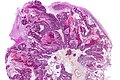
CRC metastasis to cerebellum - very low mag. (WC)
IHC
Main article: Immunohistochemistry
- Carcinoma: pankeratin +ve.
- Lung adenocarcinoma and SCLC: TTF-1 +ve, CK7 +ve, CK20 -ve.
- Breast carcinoma: CK7 +ve, ER +ve, PR +ve, BRST2 +ve/-ve.
- Colorectal carcinoma: CK7 -ve, CK20 +ve, CDX2 +ve, TTF-1 -ve.
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: PAX8 +ve, CK7 -ve, CK20 -ve, vimentin +ve, CD10 +ve.
- Melanoma: S-100 +ve, HMB-45 +ve, Melan A +ve.
- GFAP -ve.[9]
Other glial markers (suggest primary):[9]
- OLIG2, SOX2.
Origin
Breast
- 8-30% BM.
- Triple-negative cases have a poor prognosis.
See also
References
- ↑ URL: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000769.htm. Accessed on: November 8, 2014.
- ↑ Pekmezci, M.; Perry, A. (2013). "Neuropathology of brain metastases.". Surg Neurol Int 4 (Suppl 4): S245-55. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.111302. PMID 23717796.
- ↑ Suki, D.; Khoury Abdulla, R.; Ding, M.; Khatua, S.; Sawaya, R. (Oct 2014). "Brain metastases in patients diagnosed with a solid primary cancer during childhood: experience from a single referral cancer center.". J Neurosurg Pediatr 14 (4): 372-85. doi:10.3171/2014.7.PEDS13318. PMID 25127097.
- ↑ Gavrilovic, IT.; Posner, JB. (Oct 2005). "Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology.". J Neurooncol 75 (1): 5-14. doi:10.1007/s11060-004-8093-6. PMID 16215811.
- ↑ Greenwald, J.; Heng, M. (2007). Toronto Notes for Medical Students 2007 (2007 ed.). The Toronto Notes Inc. for Medical Students Inc.. pp. NS9. ISBN 978-0968592878.
- ↑ Barnholtz-Sloan, JS.; Sloan, AE.; Davis, FG.; Vigneau, FD.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, RE. (Jul 2004). "Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the Metropolitan Detroit Cancer Surveillance System.". J Clin Oncol 22 (14): 2865-72. doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.12.149. PMID 15254054.
- ↑ Schouten, LJ.; Rutten, J.; Huveneers, HA.; Twijnstra, A. (May 2002). "Incidence of brain metastases in a cohort of patients with carcinoma of the breast, colon, kidney, and lung and melanoma.". Cancer 94 (10): 2698-705. PMID 12173339.
- ↑ Della Puppa, A.; Dal Pos, S.; Zovato, S.; Orvieto, E.; Ciccarino, P.; Manara, R.; Zustovich, F.; Berti, F. et al. (Mar 2010). "Solitary intra-ventricular brain metastasis from a breast carcinoma.". J Neurooncol 97 (1): 123-6. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9988-z. PMID 19727563.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Pekmezci, M.; Perry, A. (2013). "Neuropathology of brain metastases.". Surg Neurol Int 4 (Suppl 4): S245-55. doi:10.4103/2152-7806.111302. PMID 23717796.