Eosinophilic, solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma
| Eosinophilic, solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma | |
|---|---|
| Diagnosis in short | |
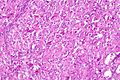
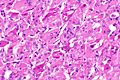
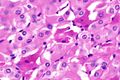
 Eosinophilic, solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma. H&E stain. | |
|
| |
| LM | epithelioid cells with abundant stippled eosinophilic cytoplasm +/- peripheral clearing, round nuclei with prominent nucleoli, nested or solid architecture +/- cystic spaces with hobnail lining cells, +/-scattered histiocytes (common), +/-multi-nucleation (common), +/-small intracytoplasmic globules |
| LM DDx | chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (eosinophilic variant), clear cell renal cell carcinoma, t(6;11) renal cell carcinoma, other renal tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm |
| IHC | PAX8 +ve, CK20 +ve, CK7 -ve, CA9 -ve, CD117 -ve, HMB-45 -ve |
| Molecular | TSC/mTOR pathway mutations |
| Gross | solid and cystic |
| Site | kidney - see kidney tumours |
|
| |
| Clinical history | women only |
| Prevalence | rare |
| Prognosis | good - data limited |
| Clin. DDx | other kidney tumours |
Eosinophilic, solid and cystic renal cell carcinoma, abbreviated ESC-RCC, is recently described, evolving kidney tumour that is presumed to be malignant.[1]
It is not within the WHO 2016 classification of renal neoplasia.
General
- Evolving entity.
- Similar to one of the three morphologic patterns of tuberous sclerosis-associated renal cell carcinoma described by Guo et al.[2]
- Women only - in the initial series.
Gross
Features:[1]
- Tan colour.
- Solid and usually cystic.
Microscopic
Features:[1]
- Epithelioid cells with abundant stippled eosinophilic cytoplasm +/- peripheral clearing.
- Round nuclei with one prominent nucleolus.
- Nested or solid architecture +/- cystic spaces with hobnail lining cells.
- +/-Scattered histiocytes (common).
- +/-Multi-nucleation (common).
- +/-Small intracytoplasmic globules - usually seen but only present in a handful of cells.
DDx:
- Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma - perinuclear halos.
- Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, eosinophilic variant - chicken-wire vessels.
- Tuberous sclerosis-associated renal cell carcinoma.
- TFEB-rearranged renal cell carcinoma.
- Other kidney tumours with eosinophilic cytoplasm.
Images
Case 1
Case 2
Case 3
Case 4
IHC
Features:[1]
- PAX8 +ve.
- CK20 +ve (14/19 cases).[3]
- CK7 -ve.
- CD117 -ve.
- CA9 -ve.
- HMB-45 -ve.
- Melan A +ve/-ve.
- Cathepsin K +ve/-ve.[4]
Molecular
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Trpkov, K.; Hes, O.; Bonert, M.; Lopez, JI.; Bonsib, SM.; Nesi, G.; Comperat, E.; Sibony, M. et al. (Sep 2015). "Eosinophilic, Solid, and Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Clinicopathologic Study of 16 Unique, Sporadic Neoplasms Occurring in Women.". Am J Surg Pathol. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000508. PMID 26414221.
- ↑ Guo, J.; Tretiakova, MS.; Troxell, ML.; Osunkoya, AO.; Fadare, O.; Sangoi, AR.; Shen, SS.; Lopez-Beltran, A. et al. (Nov 2014). "Tuberous Sclerosis-associated Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 57 Separate Carcinomas in 18 Patients.". Am J Surg Pathol 38 (11): 1457-67. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000248. PMID 25093518.
- ↑ Trpkov, K.; Abou-Ouf, H.; Hes, O.; Lopez, JI.; Nesi, G.; Comperat, E.; Sibony, M.; Osunkoya, AO. et al. (Oct 2017). "Eosinophilic Solid and Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma (ESC RCC): Further Morphologic and Molecular Characterization of ESC RCC as a Distinct Entity.". Am J Surg Pathol 41 (10): 1299-1308. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000838. PMID 28786877.
- ↑ Caliò A, Brunelli M, Gobbo S, Argani P, Munari E, Netto G, Martignoni G (May 2021). "Cathepsin K: A Novel Diagnostic and Predictive Biomarker for Renal Tumors". Cancers (Basel) 13 (10). doi:10.3390/cancers13102441. PMC 8157838. PMID 34069976. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8157838/.
- ↑ Pivovarcikova K, Alaghehbandan R, Vanecek T, Ohashi R, Pitra T, Hes O (January 2022). "TSC/mTOR Pathway Mutation Associated Eosinophilic/Oncocytic Renal Neoplasms: A Heterogeneous Group of Tumors with Distinct Morphology, Immunohistochemical Profile, and Similar Genetic Background". Biomedicines 10 (2). doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020322. PMC 8869370. PMID 35203531. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8869370/.